Increased levels of Candida albicans mannan-specific T-cell-derived antigen binding molecules in patients with invasive candidiasis
- PMID: 16603614
- PMCID: PMC1459633
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.13.4.467-474.2006
Increased levels of Candida albicans mannan-specific T-cell-derived antigen binding molecules in patients with invasive candidiasis
Abstract
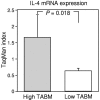
In addition to cytokines, CD4+ T cells have been found to secrete soluble, T-cell-derived antigen binding molecules (TABMs). These antigen-specific immunoproteins are thought to have immunoregulatory properties in the suppression of cell-mediated immunity (CMI) because they often associate with interleukin-10 (IL-10) and transforming growth factor beta. Decreased CMI causes susceptibility to infections caused by organisms which are normally nonpathogenic. In this situation, e.g., Candida albicans saprophytism may develop into invasive candidiasis. The difficult diagnosis of invasive candidiasis is based on the findings obtained from blood cultures and with tissue biopsy specimens, with some additional diagnostic value gained by the detection of Candida albicans mannan antigenemia and antimannan antibodies. In the present study, Candida albicans mannan-specific TABM (CAM-TABM) levels in the sera of patients with invasive candidiasis (n = 11), Candida colonization (n = 11) and noncolonization (n = 10), recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis (n = 30), and atopic eczema dermatitis syndrome (n = 59) and healthy controls (n = 30) were analyzed. For 14 participants, the effect of mannan stimulation on TABM production and gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and IL-4 mRNA expression by peripheral blood lymphocytes was also studied. It was demonstrated that CAM-TABM production was the highest in patients with invasive candidiasis and that CAM-TABM levels could distinguish Candida-colonized patients from noncolonized patients. In addition, the CAM-TABM level was directly related to mRNA expression for IL-4 but not IFN-gamma. These results reinforce the view that TABMs are associated with decreased CMI, immunoregulation, and the T-helper cell 2-type immune response.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Measurement of T-cell-derived antigen binding molecules and immunoglobulin G specific to Candida albicans mannan in sera of patients with recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis.Infect Immun. 2000 Jul;68(7):3840-7. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.7.3840-3847.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10858192 Free PMC article.
-
Candida albicans-specific lymphoproliferative and cytokine (IL-4 and IFN-gamma) responses in atopic eczema dermatitis syndrome. Evidence of CD4/CD8 and CD3/CD16+CD56 ratio elevations in vitro.Exp Dermatol. 2005 Jul;14(7):551-8. doi: 10.1111/j.0906-6705.2005.00328.x. Exp Dermatol. 2005. PMID: 15946244
-
Kinetics of anti-mannan antibodies useful in confirming invasive candidiasis in immunocompromised patients.Microbiol Immunol. 1996;40(2):125-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1996.tb03327.x. Microbiol Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8867608
-
Initiation of T-helper cell immunity to Candida albicans by IL-12: the role of neutrophils.Chem Immunol. 1997;68:110-35. doi: 10.1159/000058688. Chem Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9329219 Review.
-
Candida mannan: chemistry, suppression of cell-mediated immunity, and possible mechanisms of action.Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jan;4(1):1-19. doi: 10.1128/CMR.4.1.1. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991. PMID: 2004345 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Activation pattern of neutrophils from blood of elderly individuals with Candida-related denture stomatitis.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012 Jun;31(6):1271-7. doi: 10.1007/s10096-011-1439-z. Epub 2011 Nov 26. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22120419
References
-
- Abbas, A. K., K. M. Murphy, and A. Sher. 1996. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature 383:787-793. - PubMed
-
- Buttenschoen, K., D. C. Buttenschoen, D. Berger, C. Vasilescu, S. Schafheutle, B. Goeltenboth, M. Seidelmann, and H. G. Beger. 2001. Endotoxemia and acute-phase proteins in major abdominal surgery. Am. J. Surg. 181:36-43. - PubMed
-
- Carvalho, L. P., O. Bacellar, N. Neves, A. R. de Jesus, and E. M. Carvalho. 2002. Downregulation of IFN-gamma production in patients with recurrent vaginal candidiasis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 109:102-105. - PubMed
-
- Cone, R. E., G. M. Georgiou, and C. H. Little. 2002. Soluble T-lymphocyte antigen-specific immunoproteins: a progress report. Exp. Biol. Med. 227:438-444. - PubMed
-
- Cone, R. E., Y. Wang, J. O'Rourke, and A. Malley. 1998. Extracellular (soluble) antigen-specific T cell proteins related to the T cell receptor for antigen (sTCRr): serologic and primary amino acid sequence similarity to T cell receptor alpha chains and association with cytokines. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 18:55-67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

