PH4 of Petunia is an R2R3 MYB protein that activates vacuolar acidification through interactions with basic-helix-loop-helix transcription factors of the anthocyanin pathway
- PMID: 16603655
- PMCID: PMC1456866
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.105.034041
PH4 of Petunia is an R2R3 MYB protein that activates vacuolar acidification through interactions with basic-helix-loop-helix transcription factors of the anthocyanin pathway
Abstract
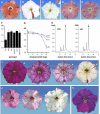
The Petunia hybrida genes ANTHOCYANIN1 (AN1) and AN2 encode transcription factors with a basic-helix-loop-helix (BHLH) and a MYB domain, respectively, that are required for anthocyanin synthesis and acidification of the vacuole in petal cells. Mutation of PH4 results in a bluer flower color, increased pH of petal extracts, and, in certain genetic backgrounds, the disappearance of anthocyanins and fading of the flower color. PH4 encodes a MYB domain protein that is expressed in the petal epidermis and that can interact, like AN2, with AN1 and the related BHLH protein JAF13 in yeast two-hybrid assays. Mutation of PH4 has little or no effect on the expression of structural anthocyanin genes but strongly downregulates the expression of CAC16.5, encoding a protease-like protein of unknown biological function. Constitutive expression of PH4 and AN1 in transgenic plants is sufficient to activate CAC16.5 ectopically. Together with the previous finding that AN1 domains required for anthocyanin synthesis and vacuolar acidification can be partially separated, this suggests that AN1 activates different pathways through interactions with distinct MYB proteins.
Figures





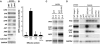
Similar articles
-
Functionally Similar WRKY Proteins Regulate Vacuolar Acidification in Petunia and Hair Development in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2016 Mar;28(3):786-803. doi: 10.1105/tpc.15.00608. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Plant Cell. 2016. PMID: 26977085 Free PMC article.
-
anthocyanin1 of petunia encodes a basic helix-loop-helix protein that directly activates transcription of structural anthocyanin genes.Plant Cell. 2000 Sep;12(9):1619-32. doi: 10.1105/tpc.12.9.1619. Plant Cell. 2000. PMID: 11006336 Free PMC article.
-
Members of an R2R3-MYB transcription factor family in Petunia are developmentally and environmentally regulated to control complex floral and vegetative pigmentation patterning.Plant J. 2011 Mar;65(5):771-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04465.x. Epub 2011 Jan 14. Plant J. 2011. PMID: 21235651
-
ANTHOCYANIN1 of petunia controls pigment synthesis, vacuolar pH, and seed coat development by genetically distinct mechanisms.Plant Cell. 2002 Sep;14(9):2121-35. doi: 10.1105/tpc.003772. Plant Cell. 2002. PMID: 12215510 Free PMC article.
-
Anthocyanin Biosynthesis Induced by MYB Transcription Factors in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 2;23(19):11701. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911701. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233003 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Target-Genes Reveal Species and Genotypic Specificity of Anthocyanin Pigmentation in Citrus and Related Genera.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jul 16;11(7):807. doi: 10.3390/genes11070807. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32708660 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analysis of a New Peanut Seed Coat Mutant for the Physiological Regulatory Mechanism Involved in Seed Coat Cracking and Pigmentation.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Oct 14;7:1491. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01491. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27790222 Free PMC article.
-
A basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor DvIVS determines flower color intensity in cyanic dahlia cultivars.Planta. 2013 Aug;238(2):331-43. doi: 10.1007/s00425-013-1897-x. Epub 2013 May 21. Planta. 2013. PMID: 23689377
-
Mechanisms and regulation of organic acid accumulation in plant vacuoles.Hortic Res. 2021 Oct 25;8(1):227. doi: 10.1038/s41438-021-00702-z. Hortic Res. 2021. PMID: 34697291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The wound-, pathogen-, and ultraviolet B-responsive MYB134 gene encodes an R2R3 MYB transcription factor that regulates proanthocyanidin synthesis in poplar.Plant Physiol. 2009 Jun;150(2):924-41. doi: 10.1104/pp.109.139071. Epub 2009 Apr 24. Plant Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19395405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avila, A., Nieto, C., Cañas, L., Benito, J., and Paz-Ares, J. (1993). Petunia hybrida genes related to the maize regulatory C1 gene and to the animal myb proto-oncogenes. Plant J. 3 553–562. - PubMed
-
- Bachem, C.W., van der Hoeven, R.S., de Bruijn, S.M., Vreugdenhil, D., Zabeau, M., and Visser, R.G. (1996). Visualization of differential gene expression using a novel method of RNA fingerprinting based on AFLP: Analysis of gene expression during potato tuber development. Plant J. 9 745–753. - PubMed
-
- Baudry, A., Heim, M.A., Dubreucq, B., Caboche, M., Weisshaar, B., and Lepiniec, L. (2004). TT2, TT8, and TTG1 synergistically specify the expression of BANYULS and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 39 366–380. - PubMed
-
- Bernhardt, C., Lee, M.M., Gonzalez, A., Zhang, F., Lloyd, A., and Schiefelbein, J. (2003). The bHLH genes GLABRA3 (GL3) and ENHANCER OF GLABRA3 (EGL3) specify epidermal cell fate in the Arabidopsis root. Development 130 6431–6439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

