RDE-4 preferentially binds long dsRNA and its dimerization is necessary for cleavage of dsRNA to siRNA
- PMID: 16603715
- PMCID: PMC1440910
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.2338706
RDE-4 preferentially binds long dsRNA and its dimerization is necessary for cleavage of dsRNA to siRNA
Abstract
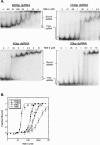
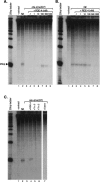
In organisms ranging from Arabidopsis to humans, Dicer requires dsRNA-binding proteins (dsRBPs) to carry out its roles in RNA interference (RNAi) and micro-RNA (miRNA) processing. In Caenorhabditis elegans, the dsRBP RDE-4 acts with Dicer during the initiation of RNAi, when long dsRNA is cleaved to small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). RDE-4 is not required in subsequent steps, and how RDE-4 distinguishes between long dsRNA and short siRNA is unclear. We report the first detailed analysis of RDE-4 binding, using purified recombinant RDE-4 and various truncated proteins. We find that, similar to other dsRBPs, RDE-4 is not sequence-specific. However, consistent with its in vivo roles, RDE-4 binds with higher affinity to long dsRNA. We also observe that RDE-4 is a homodimer in solution, and that the C-terminal domain of the protein is required for dimerization. Using extracts from wild-type and rde-4 mutant C. elegans, we show that the C-terminal dimerization domain is required for the production of siRNA. Our findings suggest a model for RDE-4 function during the initiation of RNAi.
Figures





References
-
- Andrews D., Butler J.S., Al-Bassam J., Joss L., Winn-Stapley D.A., Casjens S., Cingolani G. Bacteriophage P22 tail accessory factor GP26 is a long triple-stranded coiled-coil. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:5929–5933. - PubMed
-
- Bagga S., Bracht J., Hunter S., Massirer K., Holtz J., Eachus R., Pasquinelli A.E. Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. Cell. 2005;122:553–563. - PubMed
-
- Bass B.L., Weintraub H. A developmentally regulated activity that unwinds RNA duplexes. Cell. 1987;48:607–613. - PubMed
-
- Bass B.L., Hurst S.R., Singer J.D. Binding properties of newly identified Xenopus proteins containing dsRNA-binding motifs. Curr. Biol. 1994;4:301–314. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
