Structural insights into regulation of nuclear receptors by ligands
- PMID: 16604176
- PMCID: PMC1402225
- DOI: 10.1621/nrs.01004
Structural insights into regulation of nuclear receptors by ligands
Abstract
Nuclear receptors are DNA-binding transcription factors, the transcriptional function of many of which depends on the binding of ligands, a feature that distinguishes nuclear receptors from other transcription factors. This review will summarize recent advances in our knowledge of the interaction between selected nuclear receptors and their cognate ligands.
Figures
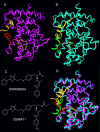
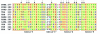
References
-
- Gampe R. T., Jr., Montana V. G., Lambert M. H., Miller A. B., Bledsoe R. K., Milburn M. V., Kliewer S. A., Willson T. M., Xu H. E. Asymmetry in the PPARgamma/RXRalpha crystal structure reveals the molecular basis of heterodimerization among nuclear receptors. Mol Cell. 2000;5:545–55. - PubMed
-
- Hu X., Lazar M. A. Transcriptional repression by nuclear hormone receptors. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2000;11:6–10. - PubMed
-
- Issemann I., Green S. Activation of a member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily by peroxisome proliferators. Nature. 1990;347:645–50. - PubMed
-
- Kallenberger B. C., Love J. D., Chatterjee V. K., Schwabe J. W. A dynamic mechanism of nuclear receptor activation and its perturbation in a human disease. Nat Struct Biol. 2003;10:136–40. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

