The effect of birth-weight with genetic susceptibility on depressive symptoms in childhood and adolescence
- PMID: 16604377
- PMCID: PMC1705530
- DOI: 10.1007/s00787-006-0545-4
The effect of birth-weight with genetic susceptibility on depressive symptoms in childhood and adolescence
Abstract
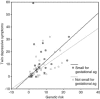
Low birth-weight has been associated with depression and related outcomes in adults, and with problem behaviours in children. This study aimed to examine the association between low birth-weight for gestation and depressive symptoms in children and adolescents and to examine whether the relationship is moderated by genetic risk for depression. An epidemiological, genetically sensitive design was used including 2,046 twins aged 8-17 years (1,023 families). Data were obtained by parental report and analysed using regression analysis. A small but significant association between birth-weight for gestation and early depressive symptoms was observed. The unit increase in depressive symptoms per unit decrease in birth-weight for gestation was greater for individuals at genetic or familial risk for depression. For low birth-weight children, genetic risk for depression moderated the influence of birth-weight for gestation in predicting early depressive symptoms. Birth-weight for gestation is moderated by genetic and familial risk for depression in influencing early depression symptoms. These observations have clinical implications in that the impact of being small for gestational age on depressive symptoms is greater in children at familial/genetic risk although the association between birth weight and depression does not imply causality.
Figures
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1093/aje/kwh122', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwh122'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15105180', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15105180/'}]}
- Andersson L, Sundstrom-Poromaa I, Wulff M, Astrom M, Bixo M (2004) Neonatal outcome following maternal antenatal depression and anxiety: a population-based study. Am J Epidemiol 159:872–881 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1097/00004583-199902000-00011', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-199902000-00011'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9951211', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9951211/'}]}
- Angold A, Costello EJ, Farmer EM, Burns BJ, Erkanli A (1999) Impaired but undiagnosed. J Am Acad Child Adoles Psy 38:129–137 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC2551118', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2551118/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '7488897', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7488897/'}]}
- Barker DJP, Osmond C, Rodin I, Fall CHD, Winter PD (1995) Low weight gain in infancy and suicide in adult life. Brit Med J 311:1203 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1001/jama.288.6.728', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.288.6.728'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12169077', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12169077/'}]}
- Bhutta AT, Cleves MA, Casey PH, Cradock MM, Arnand KJS (2002) Cognitive and behavioral outcomes of school-aged children who were born preterm: a meta-analysis. J Am Med Assoc 288:728–737 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9413793', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9413793/'}]}
- Botting N, Powls A, Cooke RWI, Marlow N (1997) Attention deficit hyperactivity disorders and other psychiatric outcomes in very low birthweight children at 12 years. J Child Psychol Psyc 38:931–941 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources