Polymorphism at position +896 of the toll-like receptor 4 gene interferes with rapid response to treatment in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 16606645
- PMCID: PMC1798301
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2006.055137
Polymorphism at position +896 of the toll-like receptor 4 gene interferes with rapid response to treatment in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
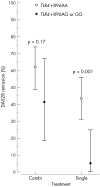
The aim of this study was to determine whether the +896 A-->G substitution of the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) gene, causing the Asp299-->Gly change in the extracellular domain of TLR4, influences treatment response in recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. 169 patients with rheumatoid arthritis were genotyped from the Finnish Rheumatoid Arthritis Combination Therapy trial, in which they were treated either with only one disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) with or without prednisolone (single group), or with three DMARDs and prednisolone (combination group). Patients homozygotic for the wild-type +896A allele were compared with those having the polymorphic G allele in terms of early clinical response (at 6 months) by the 28-joint Disease Activity Score (DAS28). 1 of 20 (5%; (95% (confidence interval (CI) 1 to 5)) patients of the single group with TLR4 +896AG or GG and 29 of 67 (43%; (95% CI 31 to 56)) patients with AA were in remission (p = 0.001). DAS28 of the single group with TLR4 +896AG or GG was higher than with AA (p = 0.019). In the combination group, remission rates and DAS28 values were comparable between the genotypes. The polymorphic TLR4 +896G allele may impair treatment response to single DMARD treatment in recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None.
Similar articles
-
Association of tumour necrosis factor a, b and c microsatellite polymorphisms with clinical disease activity and induction of remission in early rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2006 Nov-Dec;24(6):636-42. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2006. PMID: 17207378 Clinical Trial.
-
Three out of four disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug-naïve rheumatoid arthritis patients meet 28-joint Disease Activity Score remission at 12 months: results from the FIN-ERA cohort.Scand J Rheumatol. 2017 Nov;46(6):425-431. doi: 10.1080/03009742.2016.1266029. Epub 2017 Apr 3. Scand J Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28367663
-
Delay to institution of therapy and induction of remission using single-drug or combination-disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy in early rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Apr;46(4):894-8. doi: 10.1002/art.10135. Arthritis Rheum. 2002. PMID: 11953964 Clinical Trial.
-
Low-dose prednisolone in addition to the initial disease-modifying antirheumatic drug in patients with early active rheumatoid arthritis reduces joint destruction and increases the remission rate: a two-year randomized trial.Arthritis Rheum. 2005 Nov;52(11):3360-70. doi: 10.1002/art.21298. Arthritis Rheum. 2005. PMID: 16255010 Clinical Trial.
-
Response-driven combination therapy with conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs can achieve high response rates in early rheumatoid arthritis with minimal glucocorticoid and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2007 Oct;37(2):99-111. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2007.02.001. Epub 2007 Mar 27. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2007. PMID: 17391739 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Genetic variants in toll-like receptors are not associated with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility or anti-tumour necrosis factor treatment outcome.PLoS One. 2010 Dec 15;5(12):e14326. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014326. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21179534 Free PMC article.
-
Causes of DMARD withdrawal following ADR within 6 months of initiation among Indian rheumatoid arthritis patients.Rheumatol Int. 2012 Mar;32(3):743-8. doi: 10.1007/s00296-010-1646-4. Epub 2010 Dec 16. Rheumatol Int. 2012. PMID: 21161534
-
No evidence of major effects in several Toll-like receptor gene polymorphisms in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(1):R5. doi: 10.1186/ar2589. Epub 2009 Jan 13. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19134200 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Toll-like receptor 4 single-nucleotide polymorphisms Asp299Gly and Thr399Ile with the risk of primary open angle glaucoma.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2017 May;255(5):995-1001. doi: 10.1007/s00417-017-3610-4. Epub 2017 Feb 18. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28214954
-
A functional variant of TLR10 modifies the activity of NFkB and may help predict a worse prognosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Oct 4;18(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1113-z. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27716427 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arend W P. The innate immune system in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2001442224–2234. - PubMed
-
- Radstake T R D J, Roelofs M F, Jenniskens Y M, Oppers‐Walgreen B, van Riel P L, Barrrera P.et al Expression of Toll‐like receptors 2 and 4 in rheumatoid synovial tissue and regulation by proinflammatory cytokines interleukin‐12 and interleukin‐18 via interferon‐γ. Arthritis Rheum 2004503856–3865. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical