Lipoprotein oxidation in cardiovascular disease: chief culprit or innocent bystander?
- PMID: 16606677
- PMCID: PMC2118281
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20060218
Lipoprotein oxidation in cardiovascular disease: chief culprit or innocent bystander?
Abstract
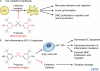
Oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is thought to contribute to atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. Consistent with this idea, the antioxidant drug probucol reduces the risk of restenosis, a form of cardiovascular disease, in humans. However, a new study now suggests that the protective effect of probucol depends not on its ability to inhibit lipid oxidation, but on its ability to induce the stress-induced antiinflammatory enzyme heme oxygenase (HO)-1. This might explain why other antioxidants, such as vitamin E, fail to prevent cardiovascular disease in humans.
Figures

Comment on
-
Antioxidants protect from atherosclerosis by a heme oxygenase-1 pathway that is independent of free radical scavenging.J Exp Med. 2006 Apr 17;203(4):1117-27. doi: 10.1084/jem.20052321. Epub 2006 Apr 10. J Exp Med. 2006. PMID: 16606673 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heinecke, J.W. 1998. Oxidants and antioxidants in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: implications for the oxidized low density lipoprotein hypothesis. Atherosclerosis. 141:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Morel, D.W., P.E. DiCorleto, and G.M. Chisolm. 1984. Endothelial and smooth muscle cells alter low density lipoprotein in vitro by free radical oxidation. Arteriosclerosis. 4:357–364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

