The polyamine binding site in inward rectifier K+ channels
- PMID: 16606689
- PMCID: PMC2151516
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.200509467
The polyamine binding site in inward rectifier K+ channels
Abstract
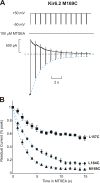
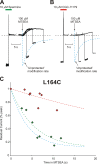
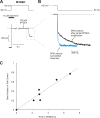
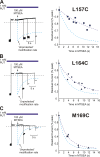
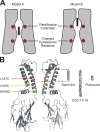
Strongly inwardly rectifying potassium channels exhibit potent and steeply voltage-dependent block by intracellular polyamines. To locate the polyamine binding site, we have examined the effects of polyamine blockade on the rate of MTSEA modification of cysteine residues strategically substituted in the pore of a strongly rectifying Kir channel (Kir6.2[N160D]). Spermine only protected cysteines substituted at a deep location in the pore, between the "rectification controller" residue (N160D in Kir6.2, D172 in Kir2.1) and the selectivity filter, against MTSEA modification. In contrast, blockade with a longer synthetic polyamine (CGC-11179) also protected cysteines substituted at sites closer to the cytoplasmic entrance of the channel. Modification of a cysteine at the entrance to the inner cavity (169C) was unaffected by either spermine or CGC-11179, and spermine was clearly "locked" into the inner cavity (i.e., exhibited a dramatically slower exit rate) following modification of this residue. These data provide physical constraints on the spermine binding site, demonstrating that spermine stably binds at a deep site beyond the "rectification controller" residue, near the extracellular entrance to the channel.
Figures





References
-
- Del Camino, D., M. Holmgren, Y. Liu, and G. Yellen. 2000. Blocker protection in the pore of a voltage-gated K+ channel and its structural implications. Nature. 403:321–325. - PubMed
-
- Dibb, K.M., T. Rose, S.Y. Makary, T.W. Claydon, D. Enkvetchakul, R. Leach, C.G. Nichols, and M.R. Boyett. 2003. Molecular basis of ion selectivity, block, and rectification of the inward rectifier Kir3.1/Kir3.4 K+ channel. J. Biol. Chem. 278:49537–49548. - PubMed
-
- Fakler, B., U. Brandle, E. Glowatzki, S. Weidemann, H.P. Zenner, and J.P. Ruppersberg. 1995. Strong voltage-dependent inward rectification of inward rectifier K+ channels is caused by intracellular spermine. Cell. 80:149–154. - PubMed
-
- Ficker, E., M. Taglialatela, B.A. Wible, C.M. Henley, and A.M. Brown. 1994. Spermine and spermidine as gating molecules for inward rectifier K+ channels. Science. 266:1068–1072. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

