Genome-wide computational prediction of transcriptional regulatory modules reveals new insights into human gene expression
- PMID: 16606704
- PMCID: PMC1457048
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.4866006
Genome-wide computational prediction of transcriptional regulatory modules reveals new insights into human gene expression
Abstract
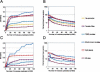
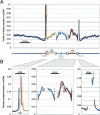
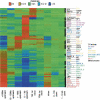
The identification of regulatory regions is one of the most important and challenging problems toward the functional annotation of the human genome. In higher eukaryotes, transcription-factor (TF) binding sites are often organized in clusters called cis-regulatory modules (CRM). While the prediction of individual TF-binding sites is a notoriously difficult problem, CRM prediction has proven to be somewhat more reliable. Starting from a set of predicted binding sites for more than 200 TF families documented in Transfac, we describe an algorithm relying on the principle that CRMs generally contain several phylogenetically conserved binding sites for a few different TFs. The method allows the prediction of more than 118,000 CRMs within the human genome. A subset of these is shown to be bound in vivo by TFs using ChIP-chip. Their analysis reveals, among other things, that CRM density varies widely across the genome, with CRM-rich regions often being located near genes encoding transcription factors involved in development. Predicted CRMs show a surprising enrichment near the 3' end of genes and in regions far from genes. We document the tendency for certain TFs to bind modules located in specific regions with respect to their target genes and identify TFs likely to be involved in tissue-specific regulation. The set of predicted CRMs, which is made available as a public database called PReMod (http://genomequebec.mcgill.ca/PReMod), will help analyze regulatory mechanisms in specific biological systems.
Figures


References
-
- Aerts S., Loo P.V., Thijs G., Moreau Y., Moor B.D., Loo P.V., Thijs G., Moreau Y., Moor B.D., Thijs G., Moreau Y., Moor B.D., Moreau Y., Moor B.D., Moor B.D.2003Computational detection of cis-regulatory modules. Bioinformatics (Suppl 2) 19II5–II14. - PubMed
-
- Aerts S., Loo P.V., Moreau Y., Moor B.D., Loo P.V., Moreau Y., Moor B.D., Moreau Y., Moor B.D., Moor B.D. A genetic algorithm for the detection of new cis-regulatory modules in sets of coregulated genes. Bioinformatics. 2004;20:1974–1976. - PubMed
-
- Alonso C.R. Hox proteins: Sculpting body parts by activating localized cell death. Curr. Biol. 2002;12:R776–R778. - PubMed
-
- Bailey T.L., Noble W.S., Noble W.S.2003Searching for statistically significant regulatory modules. Bioinformatics 19 : II16–II25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
