Catalytic and mechanical cycles in F-ATP synthases. Fourth in the Cycles Review Series
- PMID: 16607397
- PMCID: PMC1456893
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400646
Catalytic and mechanical cycles in F-ATP synthases. Fourth in the Cycles Review Series
Abstract
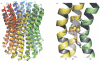
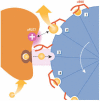
Cycles have a profound role in cellular life at all levels of organization. Well-known cycles in cell metabolism include the tricarboxylic acid and the urea cycle, in which a specific carrier substrate undergoes a sequence of chemical transformations and is regenerated at the end. Other examples include the interconversions of cofactors, such as NADH or ATP, which are present in the cell in limiting amounts and have to be recycled effectively for metabolism to continue. Every living cell performs a rapid turnover of ATP to ADP to fulfil various energetic demands and effectively regenerates the ATP from ADP in an energy-consuming process. The turnover of the ATP cycle is impressive; a human uses about its body weight in ATP per day. Enzymes perform catalytic reaction cycles in which they undergo several chemical and physical transformations before they are converted back to their original states. The ubiquitous F1F(o) ATP synthase is of particular interest not only because of its biological importance, but also owing to its unique rotational mechanism. Here, we give an overview of the membrane-embedded F(o) sector, particularly with respect to the recent crystal structure of the c ring from Ilyobacter tartaricus, and summarize current hypotheses for the mechanism by which rotation of the c ring is generated.
Figures





References
-
- Abrahams JP, Leslie AG, Lutter R, Walker JE (1994) Structure at 2.8 Å resolution of F1-ATPase from bovine heart mitochondria. Nature 370: 621–628 - PubMed
-
- Boyer PD (1993) The binding change mechanism for ATP synthase—some probabilities and possibilities. Biochim Biophys Acta 1140: 215–250 - PubMed
-
- Boyer PD (1997) The ATP synthase—a splendid molecular machine. Annu Rev Biochem 66: 717–749 - PubMed
-
- Capaldi RA, Aggeler R (2002) Mechanism of the F1Fo-type ATP synthase, a biological rotary motor. Trends Biochem Sci 27: 154–160 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

