Effect of NaCl and Helicobacter pylori vacuolating cytotoxin on cytokine expression and viability
- PMID: 16610017
- PMCID: PMC4087642
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i14.2174
Effect of NaCl and Helicobacter pylori vacuolating cytotoxin on cytokine expression and viability
Abstract
Aim: To determine whether Helicobacter pylori (H pylori) vacuolating cytotoxin (VacA) regulates release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1beta, IL-8, TNF-alpha, and IL-6) or alters gastric epithelial cell viability and to determine whether NaCl affects these VacA-induced changes.
Methods: Vacuolating activity was determined by measuring the uptake of neutral red into vacuoles of VacA-treated human gastric epithelial (AGS) cells. AGS cell viability was assessed by direct cell counting. Specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) and reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction(RT-PCR) were performed to examine the effects of H pylori VacA and NaCl on cell pro-inflammatory cytokine production in AGS cells. Immunohistochemical staining of gastric tissue from Mongolian gerbils was used to confirm VacA-induced pro-inflammatory cytokine production and the effects of NaCl on this VacA-induced response.
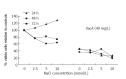
Results: Addition of VacA alone reduced AGS cell viability (P < 0.05), and this reduction was enhanced by high doses of NaCl (P < 0.05). VacA alone induced expression of TNF-alpha, IL-8 and IL-1beta, while NaCl alone induced expression of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta. Changes in mRNA levels in the presence of both VacA and NaCl were more complicated. For the case of TNF-alpha, expression was dose-dependent on NaCl. IL-6 mRNA was not detected. However, low levels of IL-6 were detected by ELISA. Positive immunohistochemical staining of IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-alpha was found in gastric tissue of H pylori-infected gerbils fed with either a normal diet or a high salt diet. However, the staining of these three cytokines was stronger in H pylori-infected animals fed with a 5 g/kg NaCl diet.
Conclusion: VacA decreases the viability of AGS cells, and this effect can be enhanced by NaCl. NaCl also affects the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines induced by VacA, suggesting that NaCl plays an important role in H pylori-induced gastric epithelial cell cytotoxicity.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Stimulation of dendritic cells with Helicobacter pylori vacuolating cytotoxin negatively regulates their maturation via the restoration of E2F1.Clin Exp Immunol. 2011 Oct;166(1):34-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04447.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21910723 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of gastric epithelial cell apoptosis by Helicobacter pylori vacuolating cytotoxin.Cancer Res. 2003 Mar 1;63(5):951-7. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12615708
-
Instrumental Role of Helicobacter pylori γ-Glutamyl Transpeptidase in VacA-Dependent Vacuolation in Gastric Epithelial Cells.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 25;10(6):e0131460. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131460. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26111186 Free PMC article.
-
Novel activities of the Helicobacter pylori vacuolating cytotoxin: from epithelial cells towards the immune system.Int J Med Microbiol. 2004 Apr;293(7-8):539-47. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00300. Int J Med Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15149029 Review.
-
Vacuolating cytotoxin A (VacA) - A multi-talented pore-forming toxin from Helicobacter pylori.Toxicon. 2016 Aug;118:27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2016.04.037. Epub 2016 Apr 20. Toxicon. 2016. PMID: 27105670 Review.
Cited by
-
Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: factors that modulate disease risk.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010 Oct;23(4):713-39. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00011-10. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20930071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fucoidan from Sargassum hemiphyllum inhibits infection and inflammation of Helicobacter pylori.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 10;12(1):429. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-04151-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35013458 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional profiling of gastric epithelial cells infected with wild type or arginase-deficient Helicobacter pylori.BMC Microbiol. 2012 Aug 13;12:175. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-175. BMC Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22889111 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation and epigenetic changes during gastric carcinogenesis.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Dec 7;21(45):12742-56. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i45.12742. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26668499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gastric cancer patients display a distinctive population of IFNg+IL10+ double positive CD8 T cells, which persists longer during prolonged activation.Exp Cell Res. 2019 Sep 15;382(2):111487. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.06.032. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Exp Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 31260655 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sun J, Misumi J, Shimaoka A, Aoki K, Esaki F. Stomach cancer-related mortality. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2001;10:61–67. - PubMed
-
- Sun J, Misumi J, Shimaoka A, Aoki K, Kono A. Stomach cancer-related mortality rate is higher in young Japanese women than in men. Public Health. 2002;116:39–44. - PubMed
-
- Cover TL, Krishna US, Israel DA, Peek RM. Induction of gastric epithelial cell apoptosis by Helicobacter pylori vacuolating cytotoxin. Cancer Res. 2003;63:951–957. - PubMed
-
- Shirin H, Sordillo EM, Oh SH, Yamamoto H, Delohery T, Weinstein IB, Moss SF. Helicobacter pylori inhibits the G1 to S transition in AGS gastric epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 1999;59:2277–2281. - PubMed
-
- Gobert AP, Mersey BD, Cheng Y, Blumberg DR, Newton JC, Wilson KT. Cutting edge: urease release by Helicobacter pylori stimulates macrophage inducible nitric oxide synthase. J Immunol. 2002;168:6002–6006. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

