Gastrointestinal stromal tumors in a cohort of Chinese patients in Hong Kong
- PMID: 16610025
- PMCID: PMC4087650
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i14.2223
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors in a cohort of Chinese patients in Hong Kong
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the prevalence and clinical pattern of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) in Hong Kong Chinese, and to assess the impact of introduction of CD117 on the disease incidence.
Methods: From the database of the Department of Pathology of Yan Chai Hospital, 47 patients, with GISTs from September 1995 to December 2003 were included in this study. Ten GISTs were diagnosed before the introduction of CD117. The clinical features, tumor characteristics, and treatment were analyzed. Factors predicting tumor related death or recurrence were studied with Cox proportional hazard model.
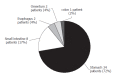
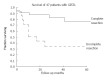
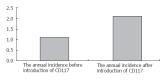
Results: The patients included 26 males and 21 females, with a mean age of 66.6 years (SD 13.1, range 29-87 years). The estimated prevalence of GISTs was 13.4-15.6 per 100,000 people, with an annual incidence of 1.68-1.96 per 100,000 people. The annual incidence of GISTs before and after the introduction of CD117 was 1.1 per 100,000 people and 2.1 per 100,000 people respectively. Stomach (34 patients, 72.3%) was the most common location for the tumor, followed by the small intestine (8 patients, 17.0%), esophagus (2 patients, 4.3%), omentum (2 patients, 4.3%) and colon (1 patient, 2.1%). Thirty-one patients (66%) had complete tumor resection. Eleven out of 16 deaths (23%) were tumor-related. The median survival time was 26 mo. Five-year survival rate was 61.3%. The significant factors associated with tumor-related death or recurrence were incomplete resection, tumor size 5 cm or above, invasion to the adjacent organ or presence of metastasis.
Conclusion: The incidence of GIST in Hong Kong is comparable to that in the United States but lower than that in Finland. The true incidence of GISTs could be underestimated before the introduction of CD117. Incomplete resection, tumor size 5 cm or above, invasion to the adjacent organ or presence of metastasis are factors predicting tumor-related death or recurrence.
Figures
References
-
- Golden T, Stoot AP. Smooth Muscle tumors of the gastrointestinal tract and retroperitoneal tissue. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1941;73:784–810.
-
- Suster S. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1996;13:297–313. - PubMed
-
- Hirota S, Isozaki K, Moriyama Y, Hashimoto K, Nishida T, Ishiguro S, Kawano K, Hanada M, Kurata A, Takeda M, et al. Gain-of-function mutations of c-kit in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science. 1998;279:577–580. - PubMed
-
- Miettinen M, Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors--definition, clinical, histological, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic features and differential diagnosis. Virchows Arch. 2001;438:1–12. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources