Advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor patients with complete response after treatment with imatinib mesylate
- PMID: 16610057
- PMCID: PMC4087685
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i13.2060
Advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor patients with complete response after treatment with imatinib mesylate
Abstract
Aim: Most gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) express constitutively activated mutant isoforms of kit kinase or platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA), which are potential therapeutic targets for imatinib mesylate (Glivec). Partial response occurred in almost two thirds of GIST patients treated with Glivec. However, complete response (CR) after Glivec therapy was sporadically reported. Here we illustrated advanced GIST patients with CR after Glivec treatment.
Methods: Between January 2001 and June 2005, 42 advanced GIST patients were treated with Glivec. Patients were administered 400 mg of Glivec in 100-mg capsules, taken orally daily with food. The response of the tumor to Glivec was evaluated after one month, three months, and every three months thereafter or whenever medical need was indicated. Each tumor of patients was investigated for mutations of kit or PDGFRA.
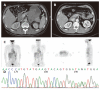
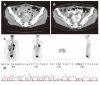
Results: The median follow-up time of the 42 advanced GIST patients treated with Glivec was 16.9 months (range, 1.0-47.0 months). Overall, 3 patients had complete response CR (7.1%), 26 partial response (67.8%), 5 stationary disease (11.9%), and 3 progressive disease (11.9%). The median duration of Glivec administration for the three patients was 36 months (range, 23-36 months). The median time to CR after Glivec treatment was 20 months (range, 9-26 months). Deletion and insertion mutations of c-kit exon 11 and insertion mutation of c-kit exon 9 were found in two cases and one case, respectively.
Conclusion: Complete response (CR) can be achi-eved in selected advanced GIST patients treated with Glivec. The median time to CR after Glivec treatment was 20 months. Deletion and insertion mutations of kit exon 11 and insertion mutation of kit exon 9 contribute to the genetic features in these selected cases.
Figures

References
-
- Lewis JJ, Brennan MF. Soft tissue sarcomas. Curr Probl Surg. 1996;33:817–872. - PubMed
-
- Rossi CR, Mocellin S, Mencarelli R, Foletto M, Pilati P, Nitti D, Lise M. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: from a surgical to a molecular approach. Int J Cancer. 2003;107:171–176. - PubMed
-
- Rossi CR, Mocellin S, Mencarelli R, Foletto M, Pilati P, Nitti D, Lise M. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: from a surgical to a molecular approach. Int J Cancer. 2003;107:171–176. - PubMed
-
- Sircar K, Hewlett BR, Huizinga JD, Chorneyko K, Berezin I, Riddell RH. Interstitial cells of Cajal as precursors of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999;23:377–389. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

