Epstein-Barr virus infection alters cellular signal cascades in human nasopharyngeal epithelial cells
- PMID: 16611410
- PMCID: PMC1578522
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.05625
Epstein-Barr virus infection alters cellular signal cascades in human nasopharyngeal epithelial cells
Abstract
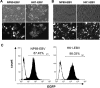
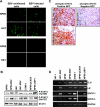
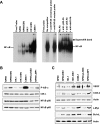
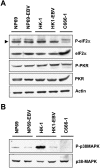
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent infection is a critical event in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) tumorigenesis. EBV-encoded genes have been shown to be involved in immune evasion and in the regulation of various cellular signaling cascades. To elucidate the roles of EBV in NPC development, stable infection of EBV in nasopharyngeal epithelial cell lines was established. Similar to primary tumors of NPC, these infected cells exhibited a type II EBV latency expression pattern. In this study, multiple cellular signaling pathways in EBV-infected cells were investigated. We first demonstrated that in vitro EBV infection resulted in the activation of STAT3 and NFkappaB signal cascades in nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. Increased expression of their downstream targets (c-Myc, Bcl-xL, IL-6, LIF, SOCS-1, SOCS-3, VEGF, and COX-2) was also observed. Moreover, EBV latent infection induced the suppression of p38-MAPK activities, but did not activate PKR cascade. Our findings suggest that EBV latent infection is able to manipulate multiple cellular signal cascades to protect infected cells from immunologic attack and to facilitate cancer development.
Figures

References
-
- Lo KW, To KF, Huang DP. Focus on nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2004;5:423–428. - PubMed
-
- Young LS, Rickinson AB. Epstein-Barr virus: 40 years on. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:757–768. - PubMed
-
- Young LS, Murray PG. Epstein-Barr virus and oncogenesis: from latent genes to tumours. Oncogene. 2003;22:5108–5121. - PubMed
-
- Portis T, Longnecker R. Epstein-Barr virus, (EBV) LMP2A mediates B-lymphocyte survival through constitutive activation of the Ras/PI3K/Akt pathway. Oncogene. 2004;23:8619–8628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
