Nanoparticle imaging of integrins on tumor cells
- PMID: 16611415
- PMCID: PMC1578521
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.05769
Nanoparticle imaging of integrins on tumor cells
Abstract
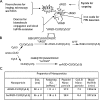
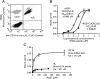
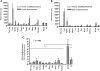
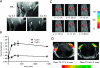
Nanoparticles 10 to 100 nm in size can deliver large payloads to molecular targets, but undergo slow diffusion and/or slow transport through delivery barriers. To examine the feasibility of nanoparticles targeting a marker expressed in tumor cells, we used the binding of cyclic arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD) nanoparticle targeting integrins on BT-20 tumor as a model system. The goals of this study were: 1) to use nanoparticles to image alpha(V)beta3 integrins expressed in BT-20 tumor cells by fluorescence-based imaging and magnetic resonance imaging, and, 2) to identify factors associated with the ability of nanoparticles to target tumor cell integrins. Three factors were identified: 1) tumor cell integrin expression (the alpha(V)beta3 integrin was expressed in BT-20 cells, but not in 9L cells); 2) nanoparticle pharmacokinetics (the cyclic RGD peptide cross-linked iron oxide had a blood half-life of 180 minutes and was able to escape from the vasculature over its long circulation time); and 3) tumor vascularization (the tumor had a dense capillary bed, with distances of <100 microm between capillaries). These results suggest that nanoparticles could be targeted to the cell surface markers expressed in tumor cells, at least in the case wherein the nanoparticles and the tumor model have characteristics similar to those of the BT-20 tumor employed here.
Figures
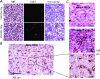
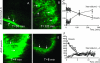
References
-
- Ferrari M. Cancer nanotechnology: opportunities and challenges. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:161–171. - PubMed
-
- NCI/NIH . Cancer Nanotechnology Plan, A Strategic Initiative to Transform Clinical Oncology and Basic Research through Directed Application of Nanotechnology. Washington, DC: 2004. pp. 8–9. ( http://nano.cancer.gov/)
-
- Moghimi SM, Hunter AC, Murray JC. Nanomedicine: current status and future prospects. FASEB J. 2005;19:311–330. - PubMed
-
- Reynolds F, O'Loughlin T, Weissleder R, Josephson L. Method of determining nanoparticle core weight. Anal Chem. 2005;77:814–817. - PubMed
-
- Zhao M, Kircher MF, Josephson L, Weissleder R. Differential conjugation of tat peptide to superparamagnetic nanoparticles and its effect on cellular uptake. Bioconjug Chem. 2002;13:840–844. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
