Yeast Gcn4p stabilization is initiated by the dissociation of the nuclear Pho85p/Pcl5p complex
- PMID: 16611745
- PMCID: PMC1483032
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-10-0975
Yeast Gcn4p stabilization is initiated by the dissociation of the nuclear Pho85p/Pcl5p complex
Abstract
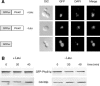
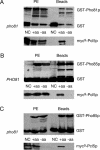
Protein stability of the c-jun-like yeast bZIP transcriptional activator Gcn4p is exclusively controlled in the yeast nucleus. Phosphorylation by the nuclear Pho85p cyclin-dependent protein kinase, a functional homolog of mammalian Cdk5, initiates the Gcn4p degradation pathway in complex with the cyclin Pcl5p. We show that the initial step in Gcn4p stabilization is the dissociation of the Pho85p/Pcl5p complex. Pcl7p, another nuclear and constantly present cyclin, is required for Gcn4p stabilization and is able to associate to Pho85p independently of the activity of the Gcn4p degradation pathway. In addition, the nuclear cyclin-dependent Pho85p kinase inhibitor Pho81p is required for Gcn4p stabilization. Pho81p only interacts with Pcl5p when Gcn4p is rapidly degraded but constitutively interacts with Pcl7p. Our data suggest that Pcl7p and Pho81p are antagonists of the Pho85p/Pcl5p complex formation in a yet unknown way, which are specifically required for Gcn4p stabilization. We suggest that dissociation of the Pho85p/Pcl5p complex as initial step in Gcn4p stabilization is a prerequisite for a shift of equilibrium to an increased amount of the Pho85p/Pcl7p complexes and subsequently results in decreased Gcn4p phosphorylation and therefore increased stability of the transcription factor.
Figures





References
-
- Andrews B., Measday V. The cyclin family of budding yeast: abundant use of a good idea. Trends Genet. 1998;14:66–72. - PubMed
-
- Brachmann C. B., Davies A., Cost G. J., Caputo E., Li J., Hieter P., Boeke J. D. Designer deletion strains derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C: a useful set of strains and plasmids for PCR-mediated gene disruption and other applications. Yeast. 1998;14:115–132. - PubMed
-
- Ching Y. P., Pang A. S., Lam W. H., Qi R. Z., Wang J. H. Identification of a neuronal Cdk5 activator-binding protein as Cdk5 inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:15237–15240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

