The unique 473HD-Chondroitinsulfate epitope is expressed by radial glia and involved in neural precursor cell proliferation
- PMID: 16611825
- PMCID: PMC6673890
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0422-06.2006
The unique 473HD-Chondroitinsulfate epitope is expressed by radial glia and involved in neural precursor cell proliferation
Abstract
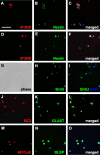
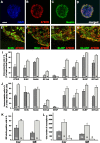
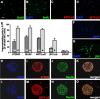
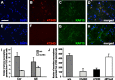
Neural stem cells have been documented in both the developing and the mature adult CNSs of mammals. This cell population holds a considerable promise for therapeutical applications in a wide array of CNS diseases. Therefore, universally applicable strategies for the purification of this population to further its cell biological characterization are sought. Here, we report that the unique chondroitin sulfate epitope recognized by the monoclonal antibody 473HD is surface expressed on actively cycling, multipotent progenitor cells of the developing telencephalon with radial glia-like properties. When used for immunopanning, the antibody enriched at least threefold for neural stem/progenitor cells characterized by the ability to self-renew as neurospheres that generated all major neural lineages in differentiation assays. In contrast, the 473HD-depleted cell fraction was mostly devoid of neurosphere-forming cells. The isolation of 473HD-positive adult multipotent progenitors from the subependymal zone of the lateral ventricle wall revealed a substantial overlap with the known adult neural stem cell marker LewisX. When the chondroitin sulfates were removed from immunoselected 473HD-positive neural stem/progenitor cell surfaces by chondroitinase ABC treatment or perturbed by the monoclonal antibody 473HD that recognizes the unique DSD-1 chondroitin sulfate epitope, the generation of neurospheres was significantly reduced. Thus, the 473HD epitope could not only be used for the isolation of multipotent neural progenitors during forebrain development as well as from the adult neurogenic niche but may also constitute a functionally important entity of the neural stem cell niche.
Figures



References
-
- Alvarez-Buylla A, Lim DA (2004). For the long run: maintaining germinal niches in the adult brain. Neuron 41:683–686. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Buylla A, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Tramontin AD (2001). A unified hypothesis on the lineage of neural stem cells. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:287–293. - PubMed
-
- Anthony TE, Klein C, Fishell G, Heintz N (2004). Radial glia serve as neuronal progenitors in all regions of the central nervous system. Neuron 41:881–890. - PubMed
-
- Bao X, Mikami T, Yamada S, Faissner A, Muramatsu T, Sugahara K (2005). Heparin-binding growth factor, pleiotrophin, mediates neuritogenic activity of embryonic pig brain-derived chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate hybrid chains. J Biol Chem 280:9180–9191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
