Lambda interferon (IFN-lambda), a type III IFN, is induced by viruses and IFNs and displays potent antiviral activity against select virus infections in vivo
- PMID: 16611910
- PMCID: PMC1472004
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.80.9.4501-4509.2006
Lambda interferon (IFN-lambda), a type III IFN, is induced by viruses and IFNs and displays potent antiviral activity against select virus infections in vivo
Abstract
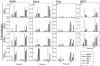
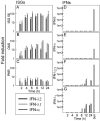
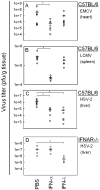
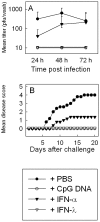
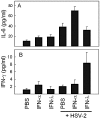
Type III interferons (IFNs) (interleukin-28/29 or lambda interferon [IFN-lambda]) are cytokines with IFN-like activities. Here we show that several classes of viruses induce expression of IFN-lambda1 and -lambda2/3 in similar patterns. The IFN-lambdas were-unlike alpha/beta interferon (IFN-alpha/beta)-induced directly by stimulation with IFN-alpha or -lambda, thus identifying type III IFNs as IFN-stimulated genes. In vitro assays revealed that IFN-lambdas have appreciable antiviral activity against encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) but limited activity against herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2), whereas IFN-alpha potently restricted both viruses. Using three murine models for generalized virus infections, we found that while recombinant IFN-alpha reduced the viral load after infection with EMCV, lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV), and HSV-2, treatment with recombinant IFN-lambda in vivo did not affect viral load after infection with EMCV or LCMV but did reduce the hepatic viral titer of HSV-2. In a model for a localized HSV-2 infection, we further found that IFN-lambda completely blocked virus replication in the vaginal mucosa and totally prevented development of disease, in contrast to IFN-alpha, which had a more modest antiviral activity. Finally, pretreatment with IFN-lambda enhanced the levels of IFN-gamma in serum after HSV-2 infection. Thus, type III IFNs are expressed in response to most viruses and display potent antiviral activity in vivo against select viruses. The discrepancy between the observed antiviral activity in vitro and in vivo may suggest that IFN-lambda exerts a significant portion of its antiviral activity in vivo via stimulation of the immune system rather than through induction of the antiviral state.
Figures

References
-
- Asselin-Paturel, C., A. Boonstra, M. Dalod, I. Durand, N. Yessaad, C. Dezutter-Dambuyant, A. Vicari, A. O'Garra, C. Biron, F. Briere, and G. Trinchieri. 2001. Mouse type I IFN-producing cells are immature APCs with plasmacytoid morphology. Nat. Immunol. 2:1144-1150. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett, N. W., K. Buttigieg, S. V. Kotenko, and G. L. Smith. 2005. Murine interferon lambdas (type III interferons) exhibit potent antiviral activity in vivo in a poxvirus infection model. J. Gen. Virol. 86:1589-1596. - PubMed
-
- Battegay, M., S. Cooper, A. Althage, J. Banziger, H. Hengartner, and R. M. Zinkernagel. 1991. Quantification of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus with an immunological focus assay in 24- or 96-well plates. J. Virol. Methods 33:191-198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

