Essential dosage-dependent functions of the transcription factor yin yang 1 in late embryonic development and cell cycle progression
- PMID: 16611997
- PMCID: PMC1447422
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.26.9.3565-3581.2006
Essential dosage-dependent functions of the transcription factor yin yang 1 in late embryonic development and cell cycle progression
Abstract
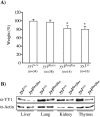
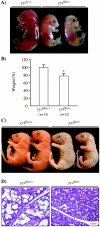
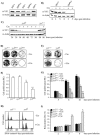
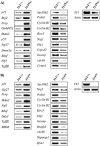
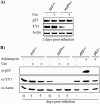
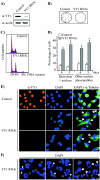
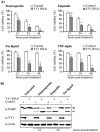
Constitutive ablation of the Yin Yang 1 (YY1) transcription factor in mice results in peri-implantation lethality. In this study, we used homologous recombination to generate knockout mice carrying yy1 alleles expressing various amounts of YY1. Phenotypic analysis of yy1 mutant embryos expressing approximately 75%, approximately 50%, and approximately 25% of the normal complement of YY1 identified a dosage-dependent requirement for YY1 during late embryogenesis. Indeed, reduction of YY1 levels impairs embryonic growth and viability in a dose-dependent manner. Analysis of the corresponding mouse embryonic fibroblast cells also revealed a tight correlation between YY1 dosage and cell proliferation, with a complete ablation of YY1 inducing cytokinesis failure and cell cycle arrest. Consistently, RNA interference-mediated inhibition of YY1 in HeLa cells prevents cytokinesis, causes proliferative arrest, and increases cellular sensitivity to various apoptotic agents. Genome-wide expression profiling identified a plethora of YY1 target genes that have been implicated in cell growth, proliferation, cytokinesis, apoptosis, development, and differentiation, suggesting that YY1 coordinates multiple essential biological processes through a complex transcriptional network. These data not only shed new light on the molecular basis for YY1 developmental roles and cellular functions, but also provide insight into the general mechanisms controlling eukaryotic cell proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation.
Figures

References
-
- Andreassen, P. R., F. B. Lacroix, O. D. Lohez, and R. L. Margolis. 2001. Neither p21WAF1 nor 14-3-3sigma prevents G2 progression to mitotic catastrophe in human colon carcinoma cells after DNA damage, but p21WAF1 induces stable G1 arrest in resulting tetraploid cells. Cancer Res. 61:7660-7668. - PubMed
-
- Austen, M., C. Cerni, J. M. Luscher-Firzlaff, and B. Luscher. 1998. YY1 can inhibit c-Myc function through a mechanism requiring DNA binding of YY1 but neither its transactivation domain nor direct interaction with c-Myc. Oncogene 17:511-520. - PubMed
-
- Austen, M., B. Luscher, and J. M. Luscher-Firzlaff. 1997. Characterization of the transcriptional regulator YY1. The bipartite transactivation domain is independent of interaction with the TATA box-binding protein, transcription factor IIB, TAFII55, or cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CPB)-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 272:1709-1717. - PubMed
-
- Bain, M., and J. Sinclair. 2005. Targeted inhibition of the transcription factor YY1 in an embryonal carcinoma cell line results in retarded cell growth, elevated levels of p53 but no increase in apoptotic cell death. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 84:543-553. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
