Neural response telemetry measures in patients implanted with Nucleus 24
- PMID: 16612529
- PMCID: PMC9442142
- DOI: 10.1016/s1808-8694(15)31271-4
Neural response telemetry measures in patients implanted with Nucleus 24
Abstract
Cochlear implantation has been recommended for children under 24 months of age. The use of objective measures is needed to help speech processor programming. The electrically evoked compound potential (EAP), which can be assessed by neural response telemetry (NRT), is one of those objective measures.
Aim: to determine how often the EAP can be recorded by NRT system during surgery and to describe the responses.
Study design: Clinical with transversal cohort.
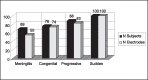
Material and method: The impedances and NRT were measured in a group of 17 Nucleus 24 implant users. The responses were analyzed and compared to the etiology, hearing loss duration and electrode array position.
Results: The EAP was easily recorded in the apical electrodes and, in otosclerosis and meningitis cases the EAP threshold was higher than in the other etiology cases.
Conclusions: The NRT can be found in 82% of the cases during surgery. The responses obtained may vary according to etiology and the position of electrodes along the cochlea.
Figures
References
-
- Mangabeira Albernaz PL. Implante coclear. Parte 2. RBM-ORL. 1996;3(2):119–122.
-
- Bento RF, Sanchez TG, Brito Neto RV. Critérios de Indicação de Implante Coclear. Arqui Otorrinolaringol. 1997;1(2):66–67.
-
- Gordon KA, Gilden JE, Ebinger KA, Shapiro WH. Neural Response Telemetry in 12- to 24-Month-Old Children. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 2002;111(189):42–48. - PubMed
-
- Seyle K & Brown CJ. Speech perception using maps based on neural response telemetry measures. Ear Hear Suppl. 2002;23(1S):72S–79S. - PubMed
-
- Gantz BJ, Brown CJ, Abbas PJ. Intraoperative measurements of electrically evoked auditory nerve compound action potential. Am J Otol. 1994;15(2):137–144. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical