Tumor-derived CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cell suppression of dendritic cell function involves TGF-beta and IL-10
- PMID: 16612596
- PMCID: PMC11030031
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-006-0160-8
Tumor-derived CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cell suppression of dendritic cell function involves TGF-beta and IL-10
Abstract
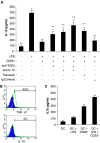
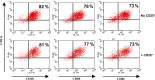
CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells have been characterized as a critical population of immunosuppressive cells. They play a crucial role in cancer progression by inhibiting the effector function of CD4(+) or CD8(+) T lymphocytes. However, whether regulatory T lymphocytes that expand during tumor progression can modulate dendritic cell function is unclear. To address this issue, we have evaluated the inhibitory potential of CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells from mice bearing a BCR-ABL(+) leukemia on bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. We present data demonstrating that CD4(+)CD25(+)FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells from tumor-bearing animals impede dendritic cell function by down-regulating the activation of the transcription factor NF-kappaB. The expression of the co-stimulatory molecules CD80, CD86 and CD40, the production of TNF-alpha, IL-12, and CCL5/RANTES by the suppressed DC is strongly down-regulated. The suppression mechanism requires TGF-beta and IL-10 and is associated with induction of the Smad signaling pathway and activation of the STAT3 transcription factor.
Figures





References
-
- Shevach EM. CD4+ CD25+ suppressor T cells: more questions than answers. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:389–400. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, et al. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. J Immunol. 1995;155:1151–1164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

