Buoyancy studies in natural communities of square gas-vacuolate archaea in saltern crystallizer ponds
- PMID: 16613609
- PMCID: PMC1459177
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-1448-2-4
Buoyancy studies in natural communities of square gas-vacuolate archaea in saltern crystallizer ponds
Abstract
Background: Possession of gas vesicles is generally considered to be advantageous to halophilic archaea: the vesicles are assumed to enable the cells to float, and thus reach high oxygen concentrations at the surface of the brine.
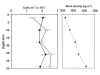
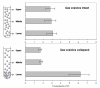
Results: We studied the possible ecological advantage of gas vesicles in a dense community of flat square extremely halophilic archaea in the saltern crystallizer ponds of Eilat, Israel. We found that in this environment, the cells' content of gas vesicles was insufficient to provide positive buoyancy. Instead, sinking/floating velocities were too low to permit vertical redistribution.
Conclusion: The hypothesis that the gas vesicles enable the square archaea to float to the surface of the brines in which they live was not supported by experimental evidence. Presence of the vesicles, which are mainly located close to the cell periphery, may provide an advantage as they may aid the cells to position themselves parallel to the surface, thereby increasing the efficiency of light harvesting by the retinal pigments in the membrane.
Figures

References
-
- Petter HFM. On bacteria of salted fish. Proc Kon Akad Wetensch Ser B. 1931;34:1417–1423.
-
- Petter HFM. PhD Thesis. University of Utrecht, The Netherlands; 1932. Over roode en andere bakteriën van gezouten visch.
-
- Houwink AL. Flagella, gas vacuoles and cell-wall structure in Halobacterium halobium: an electron microscope study. J Gen Microbiol. 1956;15:146–150. - PubMed
-
- DasSarma S, Arora P. Genetic analysis of the gas vesicle gene cluster in haloarchaea. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1997;153:1–10.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

