Direct excitation of deep dorsal horn neurones in the rat spinal cord by the activation of postsynaptic P2X receptors
- PMID: 16613873
- PMCID: PMC1779754
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.108613
Direct excitation of deep dorsal horn neurones in the rat spinal cord by the activation of postsynaptic P2X receptors
Abstract
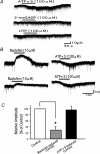
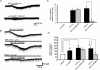
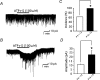
ATP mediates somatosensory transmission in the spinal cord through the activation of P2X receptors. Nonetheless, the functional significance of postsynaptic P2X receptors in spinal deep dorsal horn neurones is still not yet well understood. Using the whole-cell patch-clamp technique, we investigated whether the activation of postsynaptic P2X receptors can modulate the synaptic transmission in lamina V neurones of postnatal day (P) 9-12 spinal cord slices. At a holding potential of -70 mV, ATPgammaS (100 microm), a nonhydrolysable ATP analogue, generated an inward current, which was resistant to tetrodotoxin (1 microm) in 61% of the lamina V neurones. The ATPgammaS-induced inward current was accompanied by a significant increase in the frequency of glutamatergic miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs) in the majority of lamina V neurones. The ATPgammaS-induced inward current was not reproduced by P2Y receptor agonists, UTP (100 microm), UDP (100 microm), and 2-methylthio ADP (100 microm), and it was also not affected by the addition of guanosine-5'-O-(2-thiodiphosphate) (GDPbetaS) into the pipette solution, thus suggesting that ionotropic P2X receptors were activated by ATPgammaS instead of metabotropic P2Y receptors. On the other hand, alpha,beta-methylene ATP (100 microm) did not change any membrane current, but instead increased the mEPSC frequency in the majority of lamina V neurones. The ATPgammaS-induced inward current was suppressed by pyridoxalphosphate-6-azophenyl-2',4'-disulphonic acid (PPADS) (10 microm), but not by trinitrophenyl-ATP (TNP-ATP) (1 microm). Furthermore, we found that ATPgammaS (100 microm) produced a clear inward current which was observed in all lamina V neurones over P16 spinal cord slices, in contrast to P9-12. These results indicate that distinct subtypes of P2X receptors were functionally expressed at the post- and presynaptic sites in lamina V neurones, both of which may contribute to the hyperexcitability of lamina V in a different manner. In addition, the data relating to the developmental increase in the functional P2X receptors suggest that purinergic signalling may thus be more common in somatosensory transmission with maturation.
Figures




References
-
- Anand KJ. Effects of perinatal pain and stress. Prog Brain Res. 2000;122:117–129. - PubMed
-
- Burnstock G, Wood JN. Purinergic receptors: their role in nociception and primary afferent neurotransmission. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1996;6:526–532. - PubMed
-
- Chizh BA, Illes P. P2X receptors and nociception. Pharmacol Rev. 2001;53:553–568. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

