cAMP sensor Epac as a determinant of ATP-sensitive potassium channel activity in human pancreatic beta cells and rat INS-1 cells
- PMID: 16613879
- PMCID: PMC1779745
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.107391
cAMP sensor Epac as a determinant of ATP-sensitive potassium channel activity in human pancreatic beta cells and rat INS-1 cells
Abstract
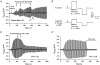
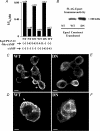
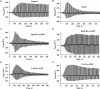
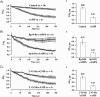
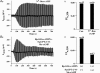
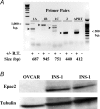
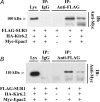
The Epac family of cAMP-regulated guanine nucleotide exchange factors (cAMPGEFs, also known as Epac1 and Epac2) mediate stimulatory actions of the second messenger cAMP on insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells. Because Epac2 is reported to interact in vitro with the isolated nucleotide-binding fold-1 (NBF-1) of the beta-cell sulphonylurea receptor-1 (SUR1), we hypothesized that cAMP might act via Epac1 and/or Epac2 to inhibit beta-cell ATP-sensitive K+ channels (K(ATP) channels; a hetero-octomer of SUR1 and Kir6.2). If so, Epac-mediated inhibition of K(ATP) channels might explain prior reports that cAMP-elevating agents promote beta-cell depolarization, Ca2+ influx and insulin secretion. Here we report that Epac-selective cAMP analogues (2'-O-Me-cAMP; 8-pCPT-2'-O-Me-cAMP; 8-pMeOPT-2'-O-Me-cAMP), but not a cGMP analogue (2'-O-Me-cGMP), inhibit the function of K(ATP) channels in human beta cells and rat INS-1 insulin-secreting cells. Inhibition of K(ATP) channels is also observed when cAMP, itself, is administered intracellularly, whereas no such effect is observed upon administration N6-Bnz-cAMP, a cAMP analogue that activates protein kinase A (PKA) but not Epac. The inhibitory actions of Epac-selective cAMP analogues at K(ATP) channels are mimicked by a cAMP agonist (8-Bromoadenosine-3', 5'-cyclic monophosphorothioate, Sp-isomer, Sp-8-Br-cAMPS), but not a cAMP antagonist (8-Bromoadenosine-3', 5'-cyclic monophosphorothioate, Rp-isomer, Rp-8-Br-cAMPS), and are abrogated following transfection of INS-1 cells with a dominant-negative Epac1 that fails to bind cAMP. Because both Epac1 and Epac2 coimmunoprecipitate with full-length SUR1 in HEK cell lysates, such findings delineate a novel mechanism of second messenger signal transduction in which cAMP acts via Epac to modulate ion channel function, an effect measurable as the inhibition of K(ATP) channel activity in pancreatic beta cells.
Figures

References
-
- Aguilar-Bryan L, Nichols CG, Wechsler SW, Clement JP, 4th, Boyd AE, 3rd, Gonzalez G, Herrera-Sosa H, Nguy K, Bryan J, Nelson DA. Cloning of the beta cell high-affinity sulfonylurea receptor: a regulator of insulin secretion. Science. 1995;268:423–426. - PubMed
-
- Asfari M, Janjic D, Meda P, Li G, Halban PA, Wollheim CB. Establishment of 2-mercaptoethanol-dependent differentiated insulin-secreting cell lines. Endocrinology. 1992;130:167–178. - PubMed
-
- Barnett DW, Pressel DM, Chern HT, Scharp DW, Misler S. cAMP-enhancing agents ‘permit’ stimulus–secretion coupling in canine pancreatic islet beta-cells. J Membr Biol. 1994;138:113–120. - PubMed
-
- Baukrowitz T, Schulte U, Oliver D, Herlitze S, Krauter T, Tucker SJ, Ruppersberg JP, Fakler B. PIP2 and PIP as determinants for ATP inhibition of KATP channels. Science. 1998;282:1141–1144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

