The effect of Vero cell coculture on the development of mouse embryos exposed to monoclonal antibodies specific for mammalian heat shock protein 60
- PMID: 16614519
- PMCID: PMC2734009
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.2.304
The effect of Vero cell coculture on the development of mouse embryos exposed to monoclonal antibodies specific for mammalian heat shock protein 60
Abstract
Heat shock proteins (HSP) have been identified as an important factor of a very complex and highly conserved cellular defense mechanism to preserve cell survival under adverse environmental conditions. HSP 60 are immunodominant antigens of microbe such as Chlamydia trachomatis and have a potentiality to become a target antigen due to antigenic similarity between chlamydial and human HSP. This study was conducted to investigate the effects of Vero cell coculture to anti-HSP 60 on the early mouse embryo development in vitro. The 2-cell mouse embryos (ICR) were cultured and mouse embryo development was observed every 24 hr for 3 days. 45% and 22.1% of the embryos cultured in Ham's F-10 plus anti HSP 60 with Vero cells developed to the 4- to 8- cell stage (day 1) and morular stage (day 2) as compared with 29.2% and 2.7% of those cultured without Vero cells respectively. But at day 3, the beneficial effect of Vero cells was not noted. These findings suggest that Vero cells have some roles to overcome the detrimental effect of anti-HSP 60 to some degree. These results suggest that Vero cells coculture will promote reproductive outcome in patient previously sensitized to microbial (e.g. Chlamydia trachomatis) HSP 60.
Figures



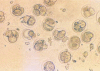
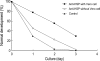
References
-
- Ritossa FA. A new puffing pattern induced by a temperature shock and DNP in Drosophila. Experientia. 1962;18:571–573.
-
- Ellis RJ. Proteins as molecular chaperones. Nature. 1987;328:378–379. - PubMed
-
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. - PubMed
-
- Soltys BJ, Gupta RS. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of the 60-kDa heat shock chaperonin protein (HSP 60) in mammalian cells. Exp Cell Res. 1996;222:16–27. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

