Impact of Ginkgo Biloba Extract EGb 761 on ischemia/reperfusion - induced oxidative stress products formation in rat forebrain
- PMID: 16614948
- PMCID: PMC11520612
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-006-9030-3
Impact of Ginkgo Biloba Extract EGb 761 on ischemia/reperfusion - induced oxidative stress products formation in rat forebrain
Abstract
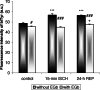
Dysbalance in reactive oxygen/nitrogen species is involved in the pathogenesis of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI). Ginkgo biloba extract (Egb 761) pre-treatment was used to observe potential antioxidant/neuroprotective effect after global ischemia/reperfusion. Egb 761 significantly decreased the level of lipoperoxidation (LPO) in rat forebrain total membrane fraction (homogenate) induced by in vitro oxidative stress (Fe(2+)+H(2)O(2)). In animals subjected to four-vessel global ischemia for 15 min and 2-24 h reperfusion the EGb pretreatment slightly decreased LPO in forebrain homogenate. However, as detected in EGb treated group, the LPO-induced lysine conjugates are attenuated in comparison to non-treated IRI animals. EGb significantly improved parameters which indicate forebrain protein oxidative damage after IRI. The intensity of tryptophane fluorescence was increased by the 18.2% comparing to non-treated IRI group and bityrosine fluorescence was significantly decreased in ischemic (21%) and 24 h reperfused (15.9%) group in comparison non-treated IRI group. In addition, the level of total free SH- groups in pre-treated animals was significantly higher comparing to non-treated animals. Our results indicate that extract of EGb 761 has potent antioxidant activity and could play a role to attenuate the IRI-induced oxidative protein modification and lipoperoxidation in the neuroprotective process.
Figures

References
-
- Chen, L. X., Chen, W. Z., Huang, H. L., Chen, L. X., and Xie, Z. Z. (1998). Protective effects of Ginkgo biloba extract against lysophosphatidylcholine-induced vascular endothelial cell damage. Acta. Pharmacol. Sin.19:359–363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

