Airway-related vagal preganglionic neurons express multiple nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits
- PMID: 16616705
- PMCID: PMC1828904
- DOI: 10.1016/j.autneu.2006.02.023
Airway-related vagal preganglionic neurons express multiple nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits
Abstract
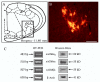
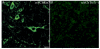
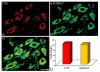
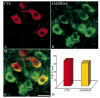
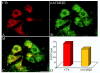
Nicotine acting centrally increases bronchomotor tone and airway secretion, suggesting that airway-related vagal preganglionic neurons (AVPNs) within the rostral nucleus ambiguus (rNA) express nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). In the present study, we examined the three main functionally characterized subtypes of nAChRs in the CNS, the alpha7 homomeric and alpha4beta2 heteromeric receptors. First, we characterized the expression of these subunits at the message (mRNA) and protein levels in brain tissues taken from the rNA region, the site where AVPNs are located. In addition, double labeling fluorescent immunohistochemistry and confocal laser microscopy were used to define the presence of alpha7, alpha4, and beta2 nAChRs on AVPNs that were retrogradely labeled with cholera toxin beta subunit (CTb), injected into the upper lung lobe (n=4) or extrathoracic trachea (n=4). Our results revealed expression of all three studied subunits at mRNA and protein levels within the rNA region. Furthermore, virtually all identified AVPNs innervating intrapulmonary airways express alpha7 and alpha4 nAChR subunits. Similarly, a majority of labeled AVPNs projecting to extrathoracic trachea contain alpha7 and beta2 subunits, but less than half of them show detectable alpha4 nAChR traits. These results suggest that AVPNs express three major nAChR subunits (alpha7, alpha4, and beta2) that could assemble into functional homologous or heterologous pentameric receptors, mediating fast and sustained nicotinic effects on cholinergic outflow to the airways.
Figures
References
-
- Agnati LF, Fuxe K. Volume transmission as a key feature of information handling in the central nervous system possible new interpretative value of the Turing’s B-type machine. Prog. Brain Res. 2000;125:3–19. - PubMed
-
- Albuquerque EX, Pereira EF, Mike A, Eisenberg HM, Maelicke A, Alkondon M. Neuronal nicotinic receptors in synaptic functions in humans and rats: physiological and clinical relevance. Behav. Brain Res. 2000;113:131–141. - PubMed
-
- Alkondon M, Albuquerque EX. The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes and their function in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex. Prog. Brain Res. 2004;145:109–120. (Review). - PubMed
-
- Alkondon M, Pereira EF, Cortes WS, Maelicke A, Albuquerque EX. Choline is a selective agonist of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the rat brain neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1997;9:2734–2742. - PubMed
-
- Alkondon M, Pereira EF, Albuquerque EX. NMDA and AMPA receptors contribute to the nicotinic cholinergic excitation of CA1 interneurons in the rat hippocampus. J. Neurophysiol. 2003;90:3–1613. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

