Dynamics of muscle glycogenolysis modeled with pH time course computation and pH-dependent reaction equilibria and enzyme kinetics
- PMID: 16617075
- PMCID: PMC1518652
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.105.073296
Dynamics of muscle glycogenolysis modeled with pH time course computation and pH-dependent reaction equilibria and enzyme kinetics
Abstract
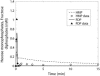
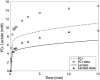
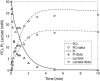
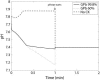
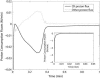
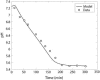
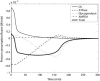
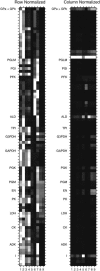
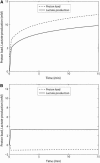
Cellular metabolites are moieties defined by their specific binding constants to H+, Mg2+, and K+ or anions without ligands. As a consequence, every biochemical reaction in the cytoplasm has an associated proton stoichiometry that is generally noninteger- and pH-dependent. Therefore, with metabolic flux, pH is altered in a medium with finite buffer capacity. Apparent equilibrium constants and maximum enzyme velocities, which are functions of pH, are also altered. We augmented an earlier mathematical model of skeletal muscle glycogenolysis with pH-dependent enzyme kinetics and reaction equilibria to compute the time course of pH changes. Analysis shows that kinetics and final equilibrium states of the closed system are highly constrained by the pH-dependent parameters. This kinetic model of glycogenolysis, coupled to creatine kinase and adenylate kinase, simulated published experiments made with a cell-free enzyme mixture to reconstitute the network and to synthesize PCr and lactate in vitro. Using the enzyme kinetic and thermodynamic data in the literature, the simulations required minimal adjustments of parameters to describe the data. These results show that incorporation of appropriate physical chemistry of the reactions with accurate kinetic modeling gives a reasonable simulation of experimental data and is necessary for a physically correct representation of the metabolic network. The approach is general for modeling metabolic networks beyond the specific pathway and conditions presented here.
Figures
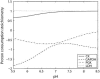
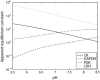
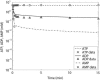
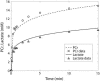




References
-
- George, P., and R. J. Rutan. 1960. The high energy phosphate bond. Concept. Prog. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 10:2–53. - PubMed
-
- George, P., R. C. Phillips, and R. J. Rutman. 1963. Estimates of thermodynamic data for the formation of Mg2+ complexes of ATP and ADP at zero ionic strength. Biochemistry. 2:508–512. - PubMed
-
- Smith, R. M., and R. A. Alberty. 1956. The apparent stability constants of ionic complexes of various adenosine phosphates with divalent cations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 78:2376–2384.
-
- Alberty, R. A. 2004. A short history of the thermodynamics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. J. Biol. Chem. 279:27831–27836. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

