Wound conditioning of a deep tissue defect including exposed bone after tumour excision using PROMOGRAN* Matrix, a protease-modulating matrix
- PMID: 16618330
- PMCID: PMC7951749
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-4801.2005.00120.x
Wound conditioning of a deep tissue defect including exposed bone after tumour excision using PROMOGRAN* Matrix, a protease-modulating matrix
Abstract
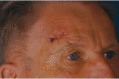
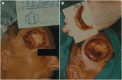
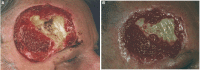
A case study reporting on the successful treatment of a patient affected by a basal cell carcinoma is submitted. Because the carcinoma had infiltrated deeply, a wide excision was necessary, including the removal of bone tissue. The deep tissue defect was treated with PROMOGRAN* Matrix, a protease-modulating matrix, to promote granulation and ensure that the skin graft do survive and heal successfully. In this case study, a rapid development of granulation tissue on the exposed surface of the bone was observed. The benefits of the dressing enabled a successful split-thickness skin grafting to be carried out which gave very good aesthetic and functional results.
Figures


References
-
- Breuninger H, Schaumburg‐Lever G. Control of excisional margins by conventional histopathological techniques in the treatment of skin tumours. An alternative to Moh's technique. J Pathol 1988;154(2):167–71. - PubMed
-
- Oishi SN, Luce EA. The difficult scalp and skull wound. Clin Plast Surg 1995;22(1):51–9. - PubMed
-
- Kirsner RS, Falanga V, Eaglstein WH. The biology of skin grafts. Skin grafts as pharmacological agents. Arch Dermatol 1993;129(4):481–3. - PubMed
-
- Dinehart SM, Dodge R, Stanley WE, Franks HH, Pollack SV. Basal cell carcinoma treated with Mohs surgery. A comparism of 54 younger patients with 1050 older patients. J Dermatol Surg Oncol 1992;18: 560–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

