Length-dependent prediction of protein intrinsic disorder
- PMID: 16618368
- PMCID: PMC1479845
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-208
Length-dependent prediction of protein intrinsic disorder
Abstract
Background: Due to the functional importance of intrinsically disordered proteins or protein regions, prediction of intrinsic protein disorder from amino acid sequence has become an area of active research as witnessed in the 6th experiment on Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction (CASP6). Since the initial work by Romero et al. (Identifying disordered regions in proteins from amino acid sequences, IEEE Int. Conf. Neural Netw., 1997), our group has developed several predictors optimized for long disordered regions (>30 residues) with prediction accuracy exceeding 85%. However, these predictors are less successful on short disordered regions (< or =30 residues). A probable cause is a length-dependent amino acid compositions and sequence properties of disordered regions.
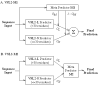
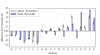
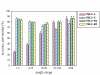
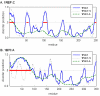
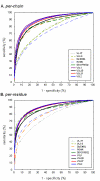
Results: We proposed two new predictor models, VSL2-M1 and VSL2-M2, to address this length-dependency problem in prediction of intrinsic protein disorder. These two predictors are similar to the original VSL1 predictor used in the CASP6 experiment. In both models, two specialized predictors were first built and optimized for short (< or = 30 residues) and long disordered regions (>30 residues), respectively. A meta predictor was then trained to integrate the specialized predictors into the final predictor model. As the 10-fold cross-validation results showed, the VSL2 predictors achieved well-balanced prediction accuracies of 81% on both short and long disordered regions. Comparisons over the VSL2 training dataset via 10-fold cross-validation and a blind-test set of unrelated recent PDB chains indicated that VSL2 predictors were significantly more accurate than several existing predictors of intrinsic protein disorder.
Conclusion: The VSL2 predictors are applicable to disordered regions of any length and can accurately identify the short disordered regions that are often misclassified by our previous disorder predictors. The success of the VSL2 predictors further confirmed the previously observed differences in amino acid compositions and sequence properties between short and long disordered regions, and justified our approaches for modelling short and long disordered regions separately. The VSL2 predictors are freely accessible for non-commercial use at http://www.ist.temple.edu/disprot/predictorVSL2.php.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

