Histone and DNA methylation defects at Hox genes in mice expressing a SET domain-truncated form of Mll
- PMID: 16618927
- PMCID: PMC1440589
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0507425103
Histone and DNA methylation defects at Hox genes in mice expressing a SET domain-truncated form of Mll
Abstract
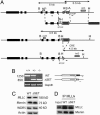
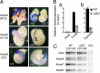
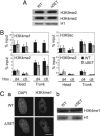
The Mll gene is a member of the mammalian trithorax group, involved with the antagonistic Polycomb group in epigenetic regulation of homeotic genes. MLL contains a highly conserved SET domain also found in various chromatin proteins. In this study, we report that mice in which this domain was deleted by homologous recombination in ES cells (DeltaSET) exhibit skeletal defects and altered transcription of particular Hox genes during development. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and bisulfite sequencing analysis on developing embryo tissues demonstrate that this change in gene expression is associated with a dramatic reduction in histone H3 Lysine 4 monomethylation and DNA methylation defects at the same Hox loci. These results establish in vivo that the major function of Mll is to act at the chromatin level to sustain the expression of selected target Hox genes during embryonic development. These observations provide previously undescribed evidence for the in vivo relationship and SET domain dependence between histone methylation and DNA methylation on MLL target genes during embryonic development.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
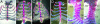

Similar articles
-
Mammalian Trithorax and polycomb-group homologues are antagonistic regulators of homeotic development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Dec 7;96(25):14372-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.25.14372. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10588712 Free PMC article.
-
MLL targets SET domain methyltransferase activity to Hox gene promoters.Mol Cell. 2002 Nov;10(5):1107-17. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00741-4. Mol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12453418
-
ASH1L Links Histone H3 Lysine 36 Dimethylation to MLL Leukemia.Cancer Discov. 2016 Jul;6(7):770-83. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0058. Epub 2016 May 6. Cancer Discov. 2016. PMID: 27154821 Free PMC article.
-
MLL translocations, histone modifications and leukaemia stem-cell development.Nat Rev Cancer. 2007 Nov;7(11):823-33. doi: 10.1038/nrc2253. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17957188 Review.
-
Why are so many MLL lysine methyltransferases required for normal mammalian development?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Aug;76(15):2885-2898. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03143-z. Epub 2019 May 16. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31098676 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association Between Histone Methyltransferase hSETD1A and Prognosis in Patients With Triple-Negative Breast Cancer After Surgery: A Retrospective Study in the Chinese Female Population.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 May;95(21):e3783. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003783. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27227949 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic natural variation in Arabidopsis thaliana.PLoS Biol. 2007 Jul;5(7):e174. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0050174. Epub 2007 Jun 19. PLoS Biol. 2007. PMID: 17579518 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish mll gene is essential for hematopoiesis.J Biol Chem. 2011 Sep 23;286(38):33345-57. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.253252. Epub 2011 Jul 22. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21784840 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of age-related somatic mutation profiles in Chinese young lung adenocarcinoma patients.Cancer Med. 2019 Apr;8(4):1350-1358. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1839. Epub 2019 Mar 1. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 30821106 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional coordination of DNA and histone methylation.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Aug 1;6(8):a018747. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a018747. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014. PMID: 25085914 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ingham P. W. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 1998;42:423–429. - PubMed
-
- Moehrle A., Paro R. Dev. Genet. 1994;15:478–484. - PubMed
-
- Paro R. Trends Genet. 1995;11:295–297. - PubMed
-
- Paro R., Strutt H., Cavalli G. In: Novartis Found. Symp. 1998. pp. 51–61. discussion 61–66, 104–113. - PubMed
-
- Djabali M., Selleri L., Parry P., Bower M., Young B. D., Evans G. A. Nat. Genet. 1992;2:113–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

