Antithrombin-S195A factor Xa-heparin structure reveals the allosteric mechanism of antithrombin activation
- PMID: 16619025
- PMCID: PMC1456925
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601089
Antithrombin-S195A factor Xa-heparin structure reveals the allosteric mechanism of antithrombin activation
Abstract
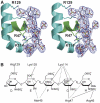
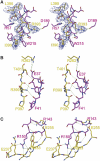
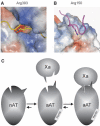
Regulation of blood coagulation is critical for maintaining blood flow, while preventing excessive bleeding or thrombosis. One of the principal regulatory mechanisms involves heparin activation of the serpin antithrombin (AT). Inhibition of several coagulation proteases is accelerated by up to 10,000-fold by heparin, either through bridging AT and the protease or by inducing allosteric changes in the properties of AT. The anticoagulant effect of short heparin chains, including the minimal AT-specific pentasaccharide, is mediated exclusively through the allosteric activation of AT towards efficient inhibition of coagulation factors (f) IXa and Xa. Here we present the crystallographic structure of the recognition (Michaelis) complex between heparin-activated AT and S195A fXa, revealing the extensive exosite contacts that confer specificity. The heparin-induced conformational change in AT is required to allow simultaneous contacts within the active site and two distinct exosites of fXa (36-loop and the autolysis loop). This structure explains the molecular basis of protease recognition by AT, and the mechanism of action of the important therapeutic low-molecular-weight heparins.
Figures



References
-
- Barlow DJ, Thornton JM (1983) Ion-pairs in proteins. J Mol Biol 168: 867–885 - PubMed
-
- Bedsted T, Swanson R, Chuang YJ, Bock PE, Bjork I, Olson ST (2003) Heparin and calcium ions dramatically enhance antithrombin reactivity with factor IXa by generating new interaction exosites. Biochemistry 42: 8143–8152 - PubMed
-
- Brunger AT, Adams PD, Clore GM, Delano WL, Gros P, GrosseKunstleve RW, Jiang JS, Kuszewski J, Nilges M, Pannu NS, Read RJ, Rice LM, Simonson T, Warren GL (1998) Crystallography & NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D 54: 905–921 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

