Arp2/3 complex-mediated actin polymerisation occurs on specific pre-existing networks in cells and requires spatial restriction to sustain functional lamellipod extension
- PMID: 16619224
- PMCID: PMC7611918
- DOI: 10.1002/cm.20131
Arp2/3 complex-mediated actin polymerisation occurs on specific pre-existing networks in cells and requires spatial restriction to sustain functional lamellipod extension
Abstract
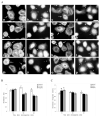
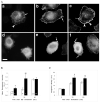
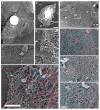
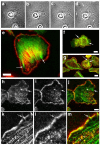
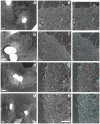
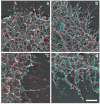
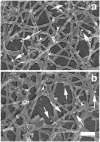
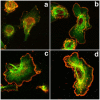
The classical Arp2/3-mediated dendritic network defines the cytoskeleton at the leading edge of crawling cells, and it is generally assumed that Arp2/3-mediated actin polymerization generates the force necessary to extend lamellipods. Our previous work suggested that successful lamellipod extension required not only free barbed ends for actin polymerization but also a proper ultrastructural organization of the cytoskeleton. To further explore the structural role of the Arp2/3 complex-mediated networks in lamellipod morphology and function, we performed a detailed analysis of the ultrastructure of the Arp2/3-mediated networks, using the WA domains of Scar and WASp to generate mislocalised Arp2/3 networks in vivo, and to reconstruct de novo Arp2/3-mediated actin nucleation and polymerization on extracted cytoskeletons. We present here evidence that spatially unrestricted Arp2/3-mediated networks are intrinsically three-dimensional and multilayered by nature and, as such, cannot sustain significant polarized extension. Furthermore, such networks polymerize only at preferred locations in extracted cells, corresponding to pre-existing Arp2/3 networks, suggesting that the specific molecular organization of the actin cytoskeleton, in terms of structure and/or biochemical composition, dictates the location of Arp2/3 complex-mediated actin polymerization. We propose that successful lamellipod extension depends not only on localized actin polymerization mediated through local signalling, but also on spatial restriction of the Arp2/3 complex-mediated nucleation of actin polymerization, both in terms of location within the cell and ultrastructural organization of the resulting network.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The F-actin side binding activity of the Arp2/3 complex is essential for actin nucleation and lamellipod extension.Curr Biol. 2001 Apr 17;11(8):620-5. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(01)00152-x. Curr Biol. 2001. PMID: 11369208
-
Relationship between Arp2/3 complex and the barbed ends of actin filaments at the leading edge of carcinoma cells after epidermal growth factor stimulation.J Cell Biol. 1999 Apr 19;145(2):331-45. doi: 10.1083/jcb.145.2.331. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10209028 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic interaction between the Arp2/3 complex and cofilin drives stimulated lamellipod extension.J Cell Sci. 2004 Jul 15;117(Pt 16):3499-510. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01211. J Cell Sci. 2004. PMID: 15252126 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of actin filament network formation through ARP2/3 complex: activation by a diverse array of proteins.Annu Rev Biochem. 2001;70:649-76. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.70.1.649. Annu Rev Biochem. 2001. PMID: 11395419 Review.
-
How is actin polymerization nucleated in vivo?Trends Cell Biol. 2001 Jul;11(7):288-93. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(01)02008-6. Trends Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11413039 Review.
Cited by
-
Arp2 depletion inhibits sheet-like protrusions but not linear protrusions of fibroblasts and lymphocytes.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2008 Nov;65(11):904-22. doi: 10.1002/cm.20312. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2008. PMID: 18720401 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of cofilin in cell locomotion and invasion.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jul;14(7):405-15. doi: 10.1038/nrm3609. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23778968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The shape of motile cells.Curr Biol. 2009 Sep 15;19(17):R762-71. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.06.053. Curr Biol. 2009. PMID: 19906578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Nance-Horan syndrome protein encodes a functional WAVE homology domain (WHD) and is important for co-ordinating actin remodelling and maintaining cell morphology.Hum Mol Genet. 2010 Jun 15;19(12):2421-32. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq125. Epub 2010 Mar 23. Hum Mol Genet. 2010. PMID: 20332100 Free PMC article.
-
Cell motility: the integrating role of the plasma membrane.Eur Biophys J. 2011 Sep;40(9):1013-27. doi: 10.1007/s00249-011-0741-0. Epub 2011 Aug 11. Eur Biophys J. 2011. PMID: 21833780 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson SI, Behrendt B, Machesky LM, Insall RH, Nash GB. Linked regulation of motility and integrin function in activated migrating neutrophils revealed by interference in remodelling of the cytoskeleton. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2003;54:135–46. - PubMed
-
- Bailly M, Ichetovkin I, Grant W, Zebda N, Machesky LM, Segall JE, Condeelis J. The F-actin side binding activity of the Arp2/3 complex is essential for actin nucleation and lamellipod extension. Curr Biol. 2001;11:620–625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

