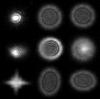
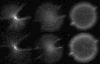
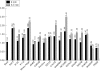
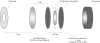Star testing: a novel evaluation of intraocular lens optical quality
- PMID: 16622088
- PMCID: PMC1857027
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.2005.082701
Star testing: a novel evaluation of intraocular lens optical quality
Abstract
Background: Despite the importance of optical quality of an intraocular lens (IOL) on visual outcomes following cataract surgery, objective data on their optical quality are not readily available, and manufacturing standards are industry regulated. The star test is a classic test of optical quality based on examination of the Airy disc and expanded diffraction rings of a point source of light, used mainly for telescope and microscope objectives.
Methods: A physical model eye cell allowed star testing of IOLs under conditions similar to the optical environment in which they operate. 18 IOLs were tested and results compared to actual images produced by these lenses in the model eye cell. Quantitative measures of star testing performance were developed.
Results: The optical performance of the IOLs varied, some performing very poorly. Most lenses (13/17) performed better in reverse orientation, while aberrations induced by the haptics of foldable IOLs were also detected. There was excellent correlation between actual images formed and star testing parameters.
Conclusion: Star testing IOLs was a novel biomedical application of a centuries old, inexpensive method. A concerning variation of optical quality was found, suggesting IOL optical performance data should be more readily available. Independent, authority mandated IOL optical quality standards should be developed, and results readily available to ophthalmologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors do not have any financial interest in the methods, materials, or any other aspect of this study.
Similar articles
-
Effect of cataract surgery incision location and intraocular lens type on ocular aberrations.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005 Apr;31(4):725-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2004.09.028. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005. PMID: 15899449
-
Imaging quality of intraocular lenses.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005 Aug;31(8):1618-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2005.01.033. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005. PMID: 16129302
-
Intraindividual comparison of aspherical and spherical intraocular lenses of same material and platform.Ophthalmology. 2009 May;116(5):896-901. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2008.11.022. Ophthalmology. 2009. PMID: 19410948 Clinical Trial.
-
[Multifocal intraocular lenses--an assessment of current status].Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1993 Jul;203(1):19-33. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1045645. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1993. PMID: 8411889 Review. German.
-
Intraocular lens optics and aberrations.Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2016 Jul;27(4):298-303. doi: 10.1097/ICU.0000000000000279. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 27093102 Review.
Cited by
-
Intraocular lens dystrophic calcification after trans-scleral diode laser treatment for a cyclodialysis cleft.Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2018 Jun 20;11:78-83. doi: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2018.06.012. eCollection 2018 Sep. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 30014050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Faaland R W, Grossman L W. Optical performance of decentered monofocal intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg 199218286–292. - PubMed
-
- International Standards Organisation Ophthalmic implants—intraocular lenses. Part 2: optical properties and test methods. EN/ISO 11979‐2 (1999)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources