Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor (HB-EGF) may improve embryonic development and implantation by increasing vitronectin receptor (integrin alphanubeta3) expression in peri-implantation mouse embryos
- PMID: 16622802
- PMCID: PMC3455038
- DOI: 10.1007/s10815-006-9021-9
Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor (HB-EGF) may improve embryonic development and implantation by increasing vitronectin receptor (integrin alphanubeta3) expression in peri-implantation mouse embryos
Abstract
Purpose: This study investigated the effects of HB-EGF on expression of integrin alphanubeta3 and implantation of embryos.
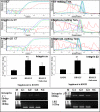
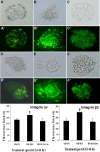
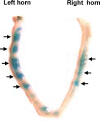
Methods: Two-cell embryos were recovered and cultured with or without 10 ng/mL HB-EGF for 96h. Expression of integrin alphanubeta3 in cultured embryos was examined by real time-RT-PCR and immunofluorescence analysis; embryos were cultured with or without HB-EGF, then transferred into the uteri of pseudo-pregnant female mice in order to analyze their implantation rate.
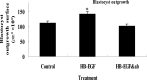
Results: HB-EGF improved embryonic hatching and outgrowth during extended culture, and up-regulated expression of integrin alphanubeta3 in both the preimplantation embryo and outgrowing blastocyst. Also, integrin alphanubeta3 subunits were localized at the pericellular borders and cell-cell contact areas. The number of successful implantation sites of transferred HB-EGF-treated embryos in the uterus was increased when compared to number of implantation sites with non-treated controls.
Conclusions: HB-EGF may improve implantation by accelerating expression of integrin alphanubeta3 in peri-implantation mouse embryos.
Figures
References
-
- Das SK, Wang XN, Paria BC, Damm D, Abraham JA, Klagsbrun M, Andrews GK, Dey SK. Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor gene is induced in the mouse uterus temporally by the blastocyst solely at the site of its apposition: a possible ligand for interaction with blastocyst EGF-receptor in implantation. Development. 1994;120:1071–1083. - PubMed
-
- Paria BC, Elenius K, Klagsbrun M, Dey SK. HB-EGF interacts with mouse blastocysts independently of ErbB1: A possible role for heparin sulfate proteoglycans and ErbB4 in blastocyst implantation. Development. 1999;126:1997–2005. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

