In-frame deletion in the EGF receptor alters kinase inhibition by gefitinib
- PMID: 16623663
- PMCID: PMC1533307
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20051962
In-frame deletion in the EGF receptor alters kinase inhibition by gefitinib
Abstract
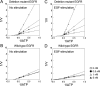
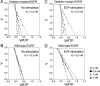
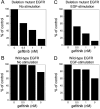
The existence of an in-frame deletion mutant correlates with the sensitivity of lung cancers to EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor)-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors. We reported previously that the in-frame 15-bp deletional mutation (delE746-A750 type deletion) was constitutively active in cells. Kinetic parameters are important for characterizing an enzyme; however, it remains unclear whether the kinetic parameters of deletion mutant EGFR are similar to those of wild-type EGFR. We analysed autophosphorylation in response to ATP and inhibition of gefitinib for deletion mutant EGFR and wild-type EGFR. Kinetic studies, examining autophosphorylation, were carried out using EGFR fractions extracted from 293-pDelta15 and 293-pEGFR cells transfected with deletion mutant EGFR and wild-type EGFR respectively. We demonstrated the difference in activities between unstimulated wild-type (K(m) for ATP=4.0+/-0.3 microM) and mutant EGFR (K(m) for ATP=2.5+/-0.2 microM). There was no difference in K(m) values between EGF-stimulated wild-type EGFR (K(m) for ATP=1.9+/-0.1 microM) and deletion mutant EGFR (K(m) for ATP=2.2+/-0.2 microM). These results suggest that mutant EGFR is active without ligand stimulation. The K(i) value for gefitinib of the deletion mutant EGFR was much lower than that of wild-type EGFR. These results suggest that the deletion mutant EGFR has a higher affinity for gefitinib than wild-type EGFR.
Figures



References
-
- Arteaga C. L. ErbB-targeted therapeutic approaches in human cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 2003;284:122–130. - PubMed
-
- Traxler P., Furet P., Mett H., Buchdunger E., Meyer T., Lydon N. Design and synthesis of novel tyrosine kinase inhibitors using a pharmacophore model of the ATP-binding site of the EGF-R. J. Pharm. Belg. 1997;52:88–96. - PubMed
-
- Shepherd F. A., Rodrigues Pereira J., Ciuleanu T., Tan E. H., Hirsh V., Thongprasert S., Campos D., Maoleekoonpiroj S., Smylie M., Martins R., et al. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005;353:123–132. - PubMed
-
- Bell D. W., Lynch T. J., Haserlat S. M., Harris P. L., Okimoto R. A., Brannigan B. W., Sgroi D. C., Muir B., Riemenschneider M. J., Iacona R. B., et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations and gene amplification in non-small-cell lung cancer: molecular analysis of the IDEAL/INTACT gefitinib trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005;23:8081–8092. - PubMed
-
- Lynch T. J., Bell D. W., Sordella R., Gurubhagavatula S., Okimoto R. A., Brannigan B. W., Harris P. L., Haserlat S. M., Supko J. G., Haluska F. G., et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

