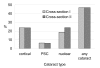
Comparison of age-specific cataract prevalence in two population-based surveys 6 years apart
- PMID: 16623958
- PMCID: PMC1524813
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2415-6-17
Comparison of age-specific cataract prevalence in two population-based surveys 6 years apart
Abstract
Background: In this study, we aimed to compare age-specific cortical, nuclear and posterior subcapsular (PSC) cataract prevalence in two surveys 6 years apart.
Methods: The Blue Mountains Eye Study examined 3654 participants (82.4% of those eligible) in cross-section I (1992-4) and 3509 participants (75.1% of survivors and 85.2% of newly eligible) in cross-section II (1997-2000, 66.5% overlap with cross-section I). Cataract was assessed from lens photographs following the Wisconsin Cataract Grading System. Cortical cataract was defined if cortical opacity comprised > or = 5% of lens area. Nuclear cataract was defined if nuclear opacity > or = Wisconsin standard 4. PSC was defined if any present. Any cataract was defined to include persons who had previous cataract surgery. Weighted kappa for inter-grader reliability was 0.82, 0.55 and 0.82 for cortical, nuclear and PSC cataract, respectively. We assessed age-specific prevalence using an interval of 5 years, so that participants within each age group were independent between the two surveys.
Results: Age and gender distributions were similar between the two populations. The age-specific prevalence of cortical (23.8% in 1st, 23.7% in 2nd) and PSC cataract (6.3%, 6.0%) was similar. The prevalence of nuclear cataract increased slightly from 18.7% to 23.9%. After age standardization, the similar prevalence of cortical (23.8%, 23.5%) and PSC cataract (6.3%, 5.9%), and the increased prevalence of nuclear cataract (18.7%, 24.2%) remained.
Conclusion: In two surveys of two population-based samples with similar age and gender distributions, we found a relatively stable cortical and PSC cataract prevalence over a 6-year period. The increased prevalence of nuclear cataract deserves further study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reproducibility of the Wisconsin cataract grading system in the Blue Mountains Eye Study.Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 1997 Sep;4(3):119-26. doi: 10.3109/09286589709115719. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 1997. PMID: 9377280
-
Prevalence of cataract in Australia: the Blue Mountains eye study.Ophthalmology. 1997 Apr;104(4):581-8. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(97)30266-8. Ophthalmology. 1997. PMID: 9111249
-
Refractive associations with cataract: the Blue Mountains Eye Study.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999 Nov;40(12):3021-6. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999. PMID: 10549667
-
The epidemiology of cataract in Australia.Am J Ophthalmol. 1999 Oct;128(4):446-65. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(99)00218-4. Am J Ophthalmol. 1999. PMID: 10577586
-
Global and regional prevalence of age-related cataract: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis.Eye (Lond). 2020 Aug;34(8):1357-1370. doi: 10.1038/s41433-020-0806-3. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Eye (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32055021 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Sources of binocular suprathreshold visual field loss in a cohort of older women being followed for risk of falls (an American Ophthalmological Society thesis).Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2007;105:312-29. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2007. PMID: 18427619 Free PMC article.
-
Cataract Surgery and Visual Acuity in Elderly Japanese: Results of Fujiwara-kyo Eye Study.Biores Open Access. 2017 Apr 1;6(1):28-34. doi: 10.1089/biores.2017.0007. eCollection 2017. Biores Open Access. 2017. PMID: 28451472 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Effect of Trigonella Foenum-Graecum on Galactose Induced Cataracts in a Rat Model; in vitro and in vivo Studies.J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2009 Oct;4(4):213-9. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2009. PMID: 23198077 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges for the cataract surgeon treating people with dementia: a qualitative study exploring anesthetic choices.Clin Ophthalmol. 2014 Sep 26;8:1993-9. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S69388. eCollection 2014. Clin Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 25328382 Free PMC article.
-
[Who visits an ophthalmologist and how often? Results of the German nationwide adult health survey (DEGS1)].Ophthalmologe. 2018 Dec;115(12):1042-1049. doi: 10.1007/s00347-017-0613-9. Ophthalmologe. 2018. PMID: 29110124 German.
References
-
- Rahmani B, Tielsch JM, Katz J, Gottsch J, Quigley H, Javitt J, Sommer A. The cause-specific prevalence of visual impairment in an urban population. The Baltimore Eye Survey. Ophthalmology. 1996;103:1721–1726. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical