Chondroitin sulfate intake inhibits the IgE-mediated allergic response by down-regulating Th2 responses in mice
- PMID: 16624819
- PMCID: PMC4140569
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M509058200
Chondroitin sulfate intake inhibits the IgE-mediated allergic response by down-regulating Th2 responses in mice
Abstract
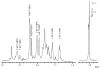
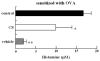
Chondroitin sulfate (CS) was administered orally to BALB/c mice immunized intraperitoneally with ovalbumin (OVA) and/or dinitrophenylated OVA. The titers of antigen-specific IgE and IgG1 in mouse sera were determined. The antigen-specific IgE production by mice fed ad libitum with CS was significantly inhibited. We also examined the effect of feeding CS on immediate-type hypersensitivity. One hour after antigen stimulation, the ears of mice fed with CS swelled less than those of the control mice. Furthermore, the rise in serum histamine in the mice fed with CS under active systemic anaphylaxis was significantly lower than that in the controls. We next examined the pattern of cytokine production by splenocytes from mice followed by re-stimulation with OVA in vitro. The splenocytes from the mice fed with CS produced less interleukin (IL)-5, IL-10, and IL-13 than those from the control group. In contrast, the production of interferon-gamma and IL-2 by the splenocytes of mice fed with CS was not significantly different from those in the control mice. In addition, the production of transforming growth factor-beta from the splenocytes of mice fed with CS was significantly higher than that of the control mice. Furthermore, we showed that the percentages of CD4(+) cells, CD8(+) cells, and CD4(+)CD25(+) cells in the splenocytes of mice fed with CS are significantly higher than those of the control. These findings suggest that oral intake of CS inhibits the specific IgE production and antigen-induced anaphylactic response by up-regulating regulatory T-cell differentiation, followed by down-regulating the Th2 response.
Figures

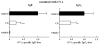

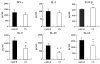
Similar articles
-
The feeding of beta-carotene down-regulates serum IgE levels and inhibits the type I allergic response in mice.Biol Pharm Bull. 2004 Jul;27(7):978-84. doi: 10.1248/bpb.27.978. Biol Pharm Bull. 2004. PMID: 15256726
-
The effect of feeding carrots on immunoglobulin E production and anaphylactic response in mice.Biol Pharm Bull. 1999 Jun;22(6):551-5. doi: 10.1248/bpb.22.551. Biol Pharm Bull. 1999. PMID: 10408224
-
Quillaja saponin can modulate ovalbumin-induced IgE allergic responses through regulation of Th1/Th2 balance in a murine model.J Agric Food Chem. 2006 May 3;54(9):3271-6. doi: 10.1021/jf060169h. J Agric Food Chem. 2006. PMID: 16637684
-
Deviation of the allergic IgE to an IgG response by gene immunotherapy.Int Rev Immunol. 1999;18(3):271-89. doi: 10.3109/08830189909043030. Int Rev Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10614729 Review.
-
Immunological activity of chondroitin sulfate.Adv Pharmacol. 2006;53:403-15. doi: 10.1016/S1054-3589(05)53019-9. Adv Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 17239777 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Development of Polyelectrolyte Complexes for the Delivery of Peptide-Based Subunit Vaccines against Group A Streptococcus.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Apr 26;10(5):823. doi: 10.3390/nano10050823. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32357402 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of natural polysaccharides on the morphology and properties of hybrid vaterite microcrystals.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 28;10(13):e33801. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33801. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39027545 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Approach to Evaluate Mechanisms That Contribute to Food Allergenicity: Comparative 2D-DIGE Analysis of Radioallergosorbent Test Positive and Negative Patients.Int J Proteomics. 2011;2011:673618. doi: 10.1155/2011/673618. Epub 2011 Sep 19. Int J Proteomics. 2011. PMID: 22091390 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of chondroitin sulfate and dermatan sulfate from various biological sources with heparin-binding growth factors and cytokines.Glycoconj J. 2013 Aug;30(6):619-32. doi: 10.1007/s10719-012-9463-5. Epub 2012 Dec 29. Glycoconj J. 2013. PMID: 23275130
-
Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects of chondroitin sulphate.J Cell Mol Med. 2009 Aug;13(8A):1451-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00826.x. Epub 2009 Jun 11. J Cell Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19522843 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marks DR, Marks LM. Postgrad Med. 1993;93:191–196. - PubMed
-
- Sampson HA. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;113:805–819. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal MK, Swanson MC, Reed CE, Yunginger JW. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984;74:687–693. - PubMed
-
- Yunginger JW. Ann Allergy. 1992;69:87–96. - PubMed
-
- Matsuo N, Yamada K, Shoji K, Mori M, Sugano M. Allergy. 1997;52:58–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

