Differential induction of BLT receptor expression on human endothelial cells by lipopolysaccharide, cytokines, and leukotriene B4
- PMID: 16624877
- PMCID: PMC1440767
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0602208103
Differential induction of BLT receptor expression on human endothelial cells by lipopolysaccharide, cytokines, and leukotriene B4
Abstract
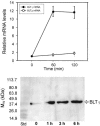
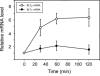
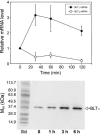
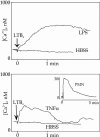
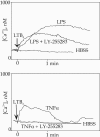
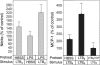
Leukotriene (LT) B4 is a powerful chemotactic and immune modulating agent that signals via two receptors denoted BLT1 and BLT2. Here we report that BLT1 and BLT2 are expressed at low levels in an apparently silent state in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). However, treatment with LPS leads to a >10 fold increase in the levels of BLT1 mRNA without any significant effects on BLT2 mRNA. In parallel, LPS also increases the amounts of BLT1 protein. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) increases the expression of BLT2 mRNA approximately 6 times above basal levels with only a modest increase in BLT1 mRNA. Interleukin-1beta causes variable and parallel increases of both BLT1 and BLT2 mRNA. The natural ligand LTB4 also increases BLT1, but not BLT2, mRNA and protein expression. Along with the induction of BLT1 and/or BLT2, HUVEC acquire the capacity to respond to LTB4 with increased levels of intracellular calcium and these signals can be blocked by isotype selective BLT antagonists, CP-105696 and LY-255283. In addition, treatment of HUVEC with LTB4 causes increased release of both nitrite, presumably reflecting nitric oxide (NO), and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. Our data indicate that expression of functional BLT receptors may occur at the surface of endothelial cells in response to LPS, cytokines, and ligand, which in turn may have functional consequences during the early vascular responses to inflammation. Moreover, the results point to BLT receptors as potential targets for pharmacological intervention in LT-dependent inflammatory diseases such as asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, and arteriosclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures

References
-
- Samuelsson B. Science. 1983;220:568–575. - PubMed
-
- Funk C. D. Science. 2001;294:1871–1875. - PubMed
-
- Ford-Hutchinson A. W., Bray M. A., Doig M. V., Shipley M. E., Smith M. J. H. Nature. 1980;286:264–265. - PubMed
-
- Malmsten C., Palmblad J., Udén A.-M., Rådmark O., Engstedt L., Samuelsson B. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1980;110:449–451. - PubMed
-
- Goodarzi K., Goodarzi M., Tager A. M., Luster A. D., von Andrian U. H. Nat. Immunol. 2003;4:965–973. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

