Mapping novel traits by array-assisted bulk segregant analysis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 16624899
- PMCID: PMC1526703
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.106.057927
Mapping novel traits by array-assisted bulk segregant analysis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
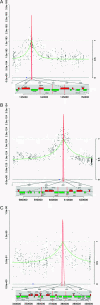
We demonstrate a new method, microarray-assisted bulk segregant analysis, for mapping traits in yeast by genotyping pooled segregants. We apply a probabilistic model to the progeny of a single cross and as little as two microarray hybridizations to reliably map an auxotrophic marker, a Mendelian trait, and a major-effect quantitative trait locus.
Figures

References
-
- Brem, R. B., G. Yvert, R. Clinton and L. Kruglyak, 2002. Genetic dissection of transcriptional regulation in budding yeast. Science 296: 752–755. - PubMed
-
- Deutschbauer, A. M., and R. W. Davis, 2005. Quantitative trait loci mapped to single-nucleotide resolution in yeast. Nat. Genet. 37: 1333–1340. - PubMed
-
- Ellis, T. P., K. G. Helfenbein, A. Tzagoloff and C. L. Dieckmann, 2004. Aep3p stabilizes the mitochondrial bicistronic mRNA encoding subunits 6 and 8 of the H+-translocating ATP synthase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 279: 15728–15733. - PubMed
-
- Gresham, D., D. M. Ruderfer, S. C. Pratt, J. Schacherer, M. J. Dunham et al., 2006. Genome-wide detection of polymorphisms at nucleotide resolution with a single DNA microarray. Science 311: 1932–1936. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

