Reversal of brain injury-induced prefrontal glutamic acid decarboxylase expression and working memory deficits by D1 receptor antagonism
- PMID: 16624944
- PMCID: PMC6673989
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4687-05.2006
Reversal of brain injury-induced prefrontal glutamic acid decarboxylase expression and working memory deficits by D1 receptor antagonism
Abstract
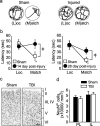
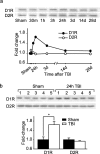
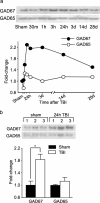
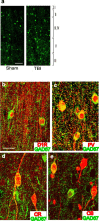
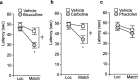
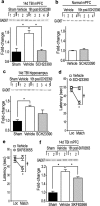
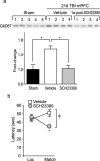
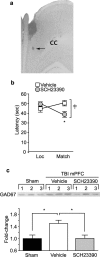
Working memory (WM), the ability to transiently hold information in mind, is essential for high-level cognitive functions that are often impaired in brain-injured patients. The cellular and molecular mechanisms contributing to WM deficits, which can manifest in the absence of overt damage, in these patients are unknown. The function of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in humans and monkeys, and the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), in rodents is critical for WM. We demonstrate that controlled cortical impact injury of rats causes a long-lasting WM impairment that is associated with increased levels of the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 (GAD67) in the mPFC for up to 1 month after injury. A single administration of dopamine D1 antagonists at 14 d after injury is sufficient to decrease GAD67 levels and restore WM for at least 1 week. These findings indicate that inhibition of prefrontal neuronal activity contributes to WM deficits and that strategies to reduce GAD67 expression can offer prolonged WM improvement in brain-injured patients.
Figures
References
-
- Akbarian S, Kim JJ, Potkin SG, Hagman JO, Tafazzoli A, Bunney WE Jr, Jones EG (1995). Gene expression for glutamic acid decarboxylase is reduced without loss of neurons in prefrontal cortex of schizophrenics. Arch Gen Psychiatry 52:258–266. - PubMed
-
- Anderson SW, Bechara A, Damasio H, Tranel D, Damasio AR (1999). Impairment of social and moral behavior related to early damage in human prefrontal cortex. Nat Neurosci 2:1032–1037. - PubMed
-
- Asada H, Kawamura Y, Maruyama K, Kume H, Ding R, Ji FY, Kanbara N, Kuzume H, Sanbo M, Yagi T, Obata K (1996). Mice lacking the 65 kDa isoform of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD65) maintain normal levels of GAD67 and GABA in their brains but are susceptible to seizures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 229:891–895. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
