A spin glass model of path integration in rat medial entorhinal cortex
- PMID: 16624947
- PMCID: PMC6674007
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4353-05.2006
A spin glass model of path integration in rat medial entorhinal cortex
Abstract
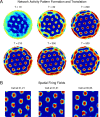
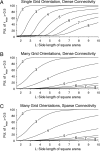
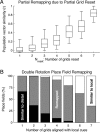
Electrophysiological recording studies in the dorsocaudal region of medial entorhinal cortex (dMEC) of the rat reveal cells whose spatial firing fields show a remarkably regular hexagonal grid pattern (Fyhn et al., 2004; Hafting et al., 2005). We describe a symmetric, locally connected neural network, or spin glass model, that spontaneously produces a hexagonal grid of activity bumps on a two-dimensional sheet of units. The spatial firing fields of the simulated cells closely resemble those of dMEC cells. A collection of grids with different scales and/or orientations forms a basis set for encoding position. Simulations show that the animal's location can easily be determined from the population activity pattern. Introducing an asymmetry in the model allows the activity bumps to be shifted in any direction, at a rate proportional to velocity, to achieve path integration. Furthermore, information about the structure of the environment can be superimposed on the spatial position signal by modulation of the bump activity levels without significantly interfering with the hexagonal periodicity of firing fields. Our results support the conjecture of Hafting et al. (2005) that an attractor network in dMEC may be the source of path integration information afferent to hippocampus.
Figures
Comment in
-
Do we understand the emergent dynamics of grid cell activity?J Neurosci. 2006 Sep 13;26(37):9352-4; discussion 9354. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.2857-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16977716 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Alyan S, McNaughton BL (1999). Hippocampectomized rats are capable of homing by path integration. Behav Neurosci 113:19–31. - PubMed
-
- Amaral DG, Ishizuka N, Claiborne B (1990). Neurons, numbers and the hippocampal network. Prog Brain Res 83:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Brown JE, Skaggs WE (2002). Concordant and discordant coding of spatial location in populations of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. J Neurophysiol 88:1605–1613. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
