Calcium supplementation for the management of primary hypertension in adults
- PMID: 16625609
- PMCID: PMC12410052
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004639.pub2
Calcium supplementation for the management of primary hypertension in adults
Abstract
Background: Metabolic studies suggest calcium may have a role in the regulation of blood pressure. Some epidemiological studies have reported that people with a higher intake of calcium tend to have lower blood pressure. Previous systematic reviews and meta-analyses have reached conflicting conclusions about whether oral calcium supplementation can reduce blood pressure.
Objectives: To evaluate the effects of oral calcium supplementation as a treatment for primary hypertension in adults.
Search strategy: We searched the Cochrane Library, MEDLINE, EMBASE, Science Citation Index, ISI Proceedings, ClinicalTrials.gov, Current Controlled Trials, CAB abstracts, and reference lists of systematic reviews, meta-analyses and randomised controlled trials (RCTs) included in the review.
Selection criteria: Inclusion criteria were: 1) RCTs comparing oral calcium supplementation with placebo, no treatment, or usual care; 2) treatment and follow-up >/=8 weeks; 3) participants over 18 years old, with raised systolic blood pressure (SBP) >/=140 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) >/=85 mmHg; 4) SBP and DBP reported at end of follow-up. We excluded trials where: participants were pregnant; received antihypertensive medication which changed during the study; or calcium supplementation was combined with other interventions.
Data collection and analysis: Two reviewers independently abstracted data and assessed trial quality. Disagreements were resolved by discussion or a third reviewer. Random effects meta-analyses and sensitivity analyses were conducted.
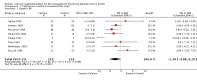
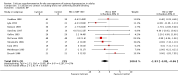
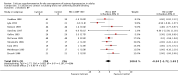
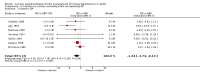
Main results: We included 13 RCTs (n=485), with between eight and 15 weeks follow-up. The results of the individual trials were heterogeneous. Combining all trials, participants receiving calcium supplementation as compared to control had a statistically significant reduction in SBP (mean difference: -2.5 mmHg, 95% CI: -4.5 to -0.6, I(2 )= 42%), but not DBP (mean difference: -0.8 mmHg, 95% CI: -2.1 to 0.4, I(2) = 48%). Sub-group analyses indicated that heterogeneity between trials could not be explained by dose of calcium or baseline blood pressure. Heterogeneity was reduced when poor quality trials were excluded. The one trial reporting adequate concealment of allocation and the one trial reporting adequate blinding yielded results consistent with the primary meta-analysis.
Authors' conclusions: In view of the poor quality of included trials and the heterogeneity between trials, the evidence in favour of causal association between calcium supplementation and blood pressure reduction is weak and is probably due to bias. This is because poor quality studies generally tend to over-estimate the effects of treatment. Larger, longer duration and better quality double-blind placebo controlled trials are needed to assess the effect of calcium supplementation on blood pressure and cardiovascular outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
None. The funding source was not in a position to benefit financially from the results of the review.
Figures














Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004639
References
References to studies included in this review
Galloe 1993 {published data only}
-
- Galloe AM, Graudal N, Moller J, Bro H, Jorgensen M, Christensen HR. Effect of oral calcium supplementation on blood pressure in patients with previously untreated hypertension: a randomised double‐blind placebo‐controlled crossover study. Journal of Human Hypertension 1993;7:43‐45. - PubMed
Grobbee 1986 {published data only}
-
- Grobbee D, Hofman A. Effect of calcium supplementation on diastolic blood pressure in young people with mild hypertension. Lancet 1986;2:703‐706. - PubMed
Kawano 1998 {published data only}
-
- Kawano Y, Yoshimi H, Matsuoka H, Takishita S, Omae T. Calcium supplementation in patients with essential hypertension: assessment by office, home and ambulatory blood pressure. Journal of Hypertension 1998;16:1693‐1699. - PubMed
Lyle 1992 {published data only}
-
- Lyle RM. Does baseline serum total calcium level influence the blood pressure response to calcium supplementation? A double‐blind study. Netherlands Journal of Medicine 1992;41:48‐55. - PubMed
Martinez 1989 {published data only}
-
- Olivan Martinez J, Perez Cano R, Miranda Garcia MJ, Montoya Garcia MJ, Moruno Garcia R, Cuenca Lopez L, Garrido Peralta M. Effect of an oral calcium supplement in the treatment of slight‐to‐ moderate essential arterial hypertension. Anales de Medicina Interna 1989;6:192‐196. - PubMed
McCarron 1985 {published data only}
-
- McCarron DA, Morris CA. Blood pressure response to oral calcium in persons with mild to moderate hypertension: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, crossover trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 1985;103:825‐831. - PubMed
Morris 1988 {published data only}
-
- Morris CD, Karanja N, McCarron DA. Dietary versus supplemental calcium to reduce blood pressure. Clinical Research 1988;36:A139.
Nowson 1989 {published data only}
-
- Nowson C, Morgan T. Effect of calcium carbonate on blood pressure in normotensive and hypertensive people. Hypertension 1989;13:630‐639. - PubMed
Sanchez 1997 {published data only}
-
- Sanchez M, Sierra A, Coca A, Poch E, Giner V, Urbano‐Marquez A. Oral calcium supplementation reduces intraplatelet free calcium concentration and insulin resistance in essential hypertensive patients. Hypertension 1997;29:531‐536. - PubMed
Strazzullo 1986 {published data only}
-
- Strazzullo P, Siani A, Gugliemi S. Controlled trial of long‐term oral calcium supplementation in essential hypertension. Hypertension 1986;8:1084‐1088. - PubMed
Takagi 1991 {published data only}
-
- Takagi Y, Fukase M, Takata S, Fujimi T, Fujita T. Calcium treatment of essential hypertension in elderly patients evaluated by 24 H monitoring. American Journal of Hypertension 1991;4:836‐839. - PubMed
Tanji 1991 {published data only}
-
- Tanji JL, Lew EY, Wong GY, Treguboff C, Ward JA, Amsterdam EA. Dietary calcium supplementation as a treatment for mild hypertension. Journal of the American Board of Family Practice 1991;4:145‐150. - PubMed
Weinberger 1993 {published data only}
-
- Weinberger MH, Wagner UL, Fineberg NS. The blood pressure effects of calcium supplementation in humans of known sodium responsiveness. American Journal of Hypertension 1993;6:799‐805. - PubMed
Zoccali 1988 {published data only}
-
- Zoccali C, Mallamaci F, Delfino D, Ciccarelli M, Parlongo S, Iellamo D, Moscato D, Maggiore Q. Double‐blind randomized crossover trial of calcium supplementation in essential hypertension. Journal of Hypertension 1988;6:451‐455. - PubMed
-
- Zoccali C, Mallamaci F, Delfino D, Ciccarellie M, Parlongo S, Iellamo D, Moscato D, Maggior Q. Long‐term oral calcium supplementation in essential hypertension: a double‐blind, randomized, crossover study. Journal of Hypertension 1986;4:S676‐S678. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Appel 1995 {published data only}
-
- Appel LJ, Hebert PR, Cohen JD, Obarzanek E, Yamamoto M, Buring J. Baseline characteristics of participants in phase II of the Trials of Hypertension Prevention (TOHP II). Annals of Epidemiology 1995;5:149‐155. - PubMed
Belizan 1983 {published data only}
-
- Belizan JM, Villar J, Pineda O, Gonzalez AE, Sainz E, Garrera G, Sibrian R. Reduction of blood pressure with calcium supplementation in young adults. JAMA 1983;249:1161‐1165. - PubMed
Buonopane 1992 {published data only}
-
- Buonopane GJ, Kilara A, Smith JS, McCarthy RD. Effect of skim milk supplementation on blood cholesterol concentration, blood pressure, and triglycerides in a free‐living human population. Journal of the American College of Nutrition 1992;11:56‐67. - PubMed
Cappuccio 1987(a) {published data only}
-
- Cappuccio FP, Markandu ND, Singer DR, Smith SJ, Shore AC, MacGregor GA. Does oral calcium supplementation lower high blood pressure? A double blind study. Journal of Hypertension 1987;5:67‐71. - PubMed
Cappuccio 1987(b) {published data only}
-
- Cappuccio FP, Elliott P, Allender PS, Pryer J, Follman DA, Cutler JA. Epidemiologic association between dietary calcium intake and blood pressure: a meta‐analysis of published data. American Journal of Epidemiology 1995;142:935‐945. - PubMed
Davis 1996 {published data only}
Feinlieb 1984 {published data only}
-
- Feinlieb M, Lenfant C, Miller SA. Hypertension and calcium. Science 1984;226:384‐386. - PubMed
Gruchow 1988 {published data only}
-
- Gruchow HW, Sobocinski KA, Barboriak JJ. Calcium intake and the relationship of dietary sodium and potassium to blood pressure. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1988;48:1463‐1470. - PubMed
Hebert 1995 {published data only}
-
- Hebert PR, Bolt RJ, Borhani NO, Cook NR, Cohen JD, Cutler JA, Hollis JF, Kuller LH, Lasser NL, Oberman A, Miller ST, Morris CA, Whelton PK, Hennekens C. Design of a multicenter trial to evaluate long‐term life‐style intervention in adults with high‐normal blood pressure levels: Trials of Hypertension Prevention (phase II). Annals of Epidemiology 1995;5:130‐139. - PubMed
Hollis 1995 {published data only}
-
- Hollis JF, Satterfield S, Smith F, Fouad M, Allender PS, Borhani N, Charleston J, Hirlinger M, King N, Schultz R, Sousoulas BG. Recruitment for Phase II of the Trials of Hypertension Prevention: effective strategies and predictors of randomization. Annals of Epidemiology 1995;5:140‐148. - PubMed
Jespersen 1993 {published data only}
-
- Jespersen B, Brock A, Pedersen EB. Lack of effect of calcium carbonate supplementation on 24th blood pressure, angiotensin II reactivity and PTH (1‐84) in essential hypertension (letter). Journal of Human Hypertension 1993;7:103‐104. - PubMed
Johnson 1985 {published data only}
-
- Johnson NE, Smith EL, Freudenheim JL. Effects on blood pressure of calcium supplementation of women. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1985;42:12‐17. - PubMed
Kromhout 1985 {published data only}
-
- Kromhout D, Bosschieter EB, Coulander CD. Potassium calcium alcohol intake and blood pressure: the Zutphen Study. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1985;41:1299‐1304. - PubMed
Kynast‐Gales 1992 {published data only}
-
- Kynast‐Gales SA, Massey LK. Effects of dietary calcium from dairy products on ambulatory blood pressure in hypertensive men. Journal of the American Dietetic Association 1992;92:1497‐1501. - PubMed
Lyle 1987 {published data only}
-
- Lyle RM, Melby CL, Hyner GC. Blood pressure and metabolic effects of calcium supplementation in normotensive white and black men. JAMA 1987;257:1772‐1776. - PubMed
Lyle 1988 {published data only}
-
- Lyle RM, Melby CL, Hyner GC. Metabolic differences between subjects whose blood pressure did or did not respond to oral calcium supplementation. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1988;47:1030‐1035. - PubMed
MacGregor 1987 {published data only}
-
- MacGregor GA, Cappuccio FP, Markandu ND. Sodium intake high blood pressure and calcium channel blockers. American Journal of Medicine 1987;82:16‐22. - PubMed
Meese 1987 {published data only}
-
- Meese RB, Gonzales DG, Casparian JM, Ram CV, Pak CM, Kaplan NM. The inconsistent effects of calcium supplements upon blood pressure in primary hypertension. American Journal of Medical Science 1987;294:219‐224. - PubMed
Morris 1992 {published data only}
-
- Morris CD, McCarron DA. Effect of calcium supplementation in an older population with mildly increased blood pressure. American Journal of Hypertension 1992;5:230‐237. - PubMed
Pan 1993 {published data only}
-
- Pan WH, Wang CY, Li LA. No significant effect of calcium and vitamin D supplementation on blood pressure and calcium metabolism in elderly Chinese. Chinese Journal of Physiology 1993;36:85‐94. - PubMed
Petersen 1994 {published data only}
-
- Petersen LJ, Rudnicki M, Hojsted J. Long‐term oral calcium supplementation reduces diastolic blood pressure in end stage renal disease: a randomized double‐blind placebo controlled study. International Journal of Artificial Organs 1994;17:37‐40. - PubMed
Sacks 1994 {published data only}
-
- Sacks FM, Hebert P, Appel LJ, Borhani NO, Applegate WB, Cohen JD, Cutler JA, Kirchner KA, Kuller LH, Roth KJ, et al. Short report: the effect of fish oil on blood pressure and high‐density lipoprotein‐cholesterol levels in phase I of the Trials of Hypertension Prevention. Journal of Hypertension 1994;12:209‐213. - PubMed
Schneider 1995 {published data only}
-
- Schneider RH, Staggers F, Alexander C, Sheppard W, Rainforth M, Kodwani K, et al. A randomized controlled trial of stress reduction for hypertension in older African Americans. Hypertension 1995;26:820‐827. - PubMed
Siani 1987 {published data only}
-
- Siani A, Strazzullo P, Guglielmi S, Mancini M. Clinical studies of the effects of different oral calcium intakes in essential hypertension. Journal of Hypertension 1987;5:S311‐S313.
Siani 1988 {published data only}
-
- Siani A, Srazzullo P, Guglielmi S, Pacioni D, Giacco A, Lacone R. Controlled trial of low calcium versus high calcium intake in mild hypertension. Journal of Hypertension 1988;6:253‐256. - PubMed
Thomsen 1987 {published data only}
-
- Thomsen K, Nilas L, Christiansen C. Dietary calcium intake and blood pressure in normotensive subjects. Acta Medica Scandinavica 1987;222:51‐56. - PubMed
TOHP 1992 {published data only}
-
- Trials of Hypertension Prevention Collaboration Research Group. The effects of nonpharmacologic interventions on blood pressure of persons with high normal levels. Results of the Trials of Hypertension Prevention, Phase I. JAMA 1992;267:1213‐1220. - PubMed
van Beresteyn 1986 {published data only}
-
- Beresteyn ECH, Schaafsma G, Waard H. Oral calcium and blood pressure: a controlled intervention trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1986;44:883‐888. - PubMed
Vinson 1987 {published data only}
-
- Vinson JA, Mazur T, Bose P. Comparison of different forms of calcium on blood pressure of normotensive young males. Nutrition Reports International 1987;36:497‐505.
Yamamoto 1995 {published data only}
-
- Yamamoto ME, Applegate WB, Klag MJ, Borhani NO, Cohen JD, Kirchner KA, et al. Trials of Hypertension Prevention (TOHP) Collaborative Research Group. Lack of blood pressure effect with calcium and magnesium supplementation in adults with high‐normal blood pressure: Results from Phase I of the Trials of Hypertension Prevention (TOHP). Annals of Epidemiology 1995;5:96‐107. - PubMed
Zemel 2005 {published data only}
-
- Zemel MB, Richards J, Mathis S, Milstead A, Gebhardt L, Silva E. Dairy augmentation of total and central fat loss in obese subjects. International Journal of Obesity 2005;29:391‐397. - PubMed
Zhou 1994 {published data only}
-
- Zhou C, Fan S, Zhou L, Yanping N, Huang T, Shi Y. Clinical observation of treatment of hypertension with calcium. American Journal of Hypertension 1994;7:363‐367. - PubMed
Zoccali 1987 {published data only}
-
- Zoccali C, Mallamaci F, Delfino D, Parlongo S, Iellamo D, Moscato D, et al. Does calcium have a dual effect on arterial pressure? Response to 1,25 dihydroxy vitamin D3 and calcium supplements in essential hypertension. Journal of Hypertension 1987;5:S267‐S269.
Additional references
Allender 1996
-
- Allender PS, Cutler JA, Follman D, Cappucio FP, Pryer J, Elliott P. Dietary calcium and blood pressure: a meta‐analysis of randomized clinical trials. Annals of Internal Medicine 1996;124:825‐831. - PubMed
Australian 1989
-
- Australian National Health and Medical Research Council Dietary Salt Study Management Committee. Effects of replacing sodium intake in subjects on a low sodium diet: a crossover study. Clinical and Experimental Hypertension 1989;A11:1011‐1024. - PubMed
BNF 2004 [Computer program]
-
- British Medical Association and Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain. British National Formulary 47. British Medical Association and Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain, 2004.
Brown 1997
Bruce 1999
Bucher 1996
-
- Bucher HC, Cook RJ, Guyatt GH, Lang J, Cook DJ, Hatala R, Hunt DL. Effects of Dietary Calcium Supplementation on Blood Pressure: A Meta‐Analysis of Randomized Control Trials. JAMA 1996;275:1016‐1022. - PubMed
Burgess 1999
Cappuccio 1989
-
- Cappuccio FP, Siani A, Strazzullo P. Oral calcium supplementation and blood pressure: an overview of randomized controlled trials. J Hypertens 1989;7:941‐946. - PubMed
Cappuccio 1995
-
- Cappuccio FP, Elliott P, Allender PS, Pryer J, Follman DA, Cutler JA. Epidemiologic association between dietary calcium intake and blood pressure: a meta‐analysis of published data. American Journal of Epidemiology 1995;142:935‐945. - PubMed
Cochrane Handbook
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins, JPT, Altman DG, editors. Analysing and presenting results. Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 4.2.5 [updated May 2005]; Section 8. Chichester, UK: The Cochrane Library, Issue 3, 2005. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2005.
Curtin 2002
-
- Curtin F, Altman DG, Elbourne D. Meta‐analysis combining parallel and cross‐over clinical trials. Stats in Medicine 2002;21:2131‐44. - PubMed
Cutler 1990
-
- Cutler JA, Brittain E. Calcium and blood pressure. An epidemiologic perspective. Am J Hypertens 2002;3:137S‐146S. - PubMed
DASH 1999
-
- Vogt TM, Appel LJ, Obarzanek E, Moore TJ, Vollmer WM, Svetkey LP, et al. Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension: rationale design and methods.. J Am Diet Assoc 1999;99:S12‐S28. - PubMed
DASH 2000
-
- Conlin PR, Chow D, Miller ER, Svetkey LP, Lin PH, Harsha DW, et al. The effect of dietary patterns on blood pressure control in hypertensive patients: results from the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) trial.. Am J Hypertens 2000;13:949‐955. - PubMed
DerSimonian 1986
-
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta‐analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 1986;7:177‐188. - PubMed
Dickersin 1994
Egger 2003
-
- Egger M, Juni P, Bartlett C, Holenstein F, Sterne J. How important are comprehensive literature searches and the assessment of trial quality in systematic reviews? Empirical study. Health Technol. Assess. 2003 2003; Vol. 7. - PubMed
Elbourne 2002
-
- Elbourne D, Altman DG, Higgins JPT, Curtin F, Worthington HV, Vail A. Meta‐analyses involving cross‐over trials: methodological issues. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002;31:140‐9. - PubMed
Griffith 1999
-
- Griffith LE, Guyatt GH, Cook RJ, Bucher HC, Cook DJ. The influence of dietary and non‐dietary calcium supplementation on blood pressure: an updated meta analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Hypertens 1999;12:84‐92. - PubMed
Hamet 1995
-
- Hamet P. The evaluation of the scientific evidence for a relationship between calcium and hypertension. J Nutr 1995;125:311S‐400S. - PubMed
Higgins 2002
-
- Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21:1539‐58. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
JNC VII 2003
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL, et al. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA 2003;289:2560‐2572. - PubMed
Juni 2001
Kawano 1998 (ii)
-
- Kawano Y, Matsuoka H, Takishita S, Omae T. Effects of magnesium supplementation in hypertensive patients: assessment by office, home and ambulatory blood pressures. Hypertension 1998;32:260‐265. - PubMed
Kotchen 1998
-
- Kotchen TA, McCarron DA. Dietary electrolytes and blood pressure: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association nutrition committee. Circulation 1998;98:613‐617. - PubMed
Law 2003
MacMahon 1990
-
- MacMahon S, Cutler PR. Blood pressure stroke and coronary heart disease. Part I prolonged differences in blood pressure: prospective observational studies corrected for the regression dilution bias. Lancet 1990;335:765‐774. - PubMed
Moher 1998
-
- Moher D, Pham B, Jones A, Cook DJ, Jadad AR, Moher M, et al. Does quality of reports of randomised trials affect estimates of intervention efficacy reported in meta‐analyses?. Lancet 1998;352:609‐613. - PubMed
NIH 2000
-
- National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group. Report on High Blood Pressure in Pregnancy. NIH Publication No 00‐3029 2000.
Nowson 1986
-
- Nowson C, Morgan T. Effect of calcium carbonate on blood pressure. Journal of Hypertension 1986;4:S673‐S675. - PubMed
PSC 2002
-
- Prospective Studies Collaboration. Age‐specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: a meta‐analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet 2002;360:1903‐1913. - PubMed
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman D. Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273:408‐412. - PubMed
Sunderrajan 1984
-
- Sunderrajan S, Bauer JH. Oral calcium supplementation does not alter blood pressure or vascular response in normotensive men. Circulation 1984;70:II‐130.
WHO 2002
-
- World Health Organization. The world health report 2002: reducing risks, promoting healthy life. Geneva: World Health Organisation, 2002.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

