The FUSE/FBP/FIR/TFIIH system is a molecular machine programming a pulse of c-myc expression
- PMID: 16628215
- PMCID: PMC1462968
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601101
The FUSE/FBP/FIR/TFIIH system is a molecular machine programming a pulse of c-myc expression
Abstract
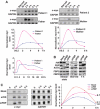
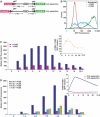
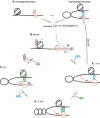
FarUpStream Element (FUSE) Binding Protein (FBP) binds the human c-myc FUSE in vitro only in single-stranded or supercoiled DNA. Because transcriptionally generated torsion melts FUSE in vitro even in linear DNA, and FBP/FBP Interacting Repressor (FIR) regulates transcription through TFIIH, these components have been speculated to be the mechanosensor (FUSE) and effectors (FBP/FIR) of a real-time mechanism controlling c-myc transcription. To ascertain whether the FUSE/FBP/FIR system operates according to this hypothesis in vivo, the flux of activators, repressors and chromatin remodeling complexes on the c-myc promoter was monitored throughout the serum-induced pulse of transcription. After transcription was switched on by conventional factors and chromatin regulators, FBP and FIR were recruited and established a dynamically remodeled loop with TFIIH at the P2 promoter. In XPB cells carrying mutant TFIIH, loop formation failed and the serum response was abnormal; RNAi depletion of FIR similarly disabled c-myc regulation. Engineering FUSE into episomal vectors predictably re-programmed metallothionein-promoter-driven reporter expression. The in vitro recruitment of FBP and FIR to dynamically stressed c-myc DNA paralleled the in vivo process.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantitative characterization of the interactions among c-myc transcriptional regulators FUSE, FBP, and FIR.Biochemistry. 2010 Jun 8;49(22):4620-34. doi: 10.1021/bi9021445. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20420426
-
The FBP interacting repressor targets TFIIH to inhibit activated transcription.Mol Cell. 2000 Feb;5(2):331-41. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80428-1. Mol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10882074
-
Dimerization of FIR upon FUSE DNA binding suggests a mechanism of c-myc inhibition.EMBO J. 2008 Jan 9;27(1):277-89. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601936. Epub 2007 Dec 6. EMBO J. 2008. PMID: 18059478 Free PMC article.
-
[Alternative Splicing Detection as Biomarker Candidates for Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment with Establishment of Clinical Biobank in Chiba University].Rinsho Byori. 2015 Mar;63(3):347-60. Rinsho Byori. 2015. PMID: 26524858 Review. Japanese.
-
c-myc expression: keep the noise down!Mol Cells. 2005 Oct 31;20(2):157-66. Mol Cells. 2005. PMID: 16267388 Review.
Cited by
-
Bullied no more: when and how DNA shoves proteins around.Q Rev Biophys. 2012 Aug;45(3):257-299. doi: 10.1017/S0033583512000054. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Q Rev Biophys. 2012. PMID: 22850561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FBPs are calibrated molecular tools to adjust gene expression.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Sep;26(17):6584-97. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00754-06. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16914741 Free PMC article.
-
Fuse binding protein antagonizes the transcription activity of tumor suppressor protein p53.BMC Cancer. 2014 Dec 8;14:925. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-925. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25487856 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of Far Upstream Element-Binding Protein 1 (FUBP1) Promotes Tumor Proliferation and Tumorigenesis of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 11;12(1):e0169852. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169852. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28076379 Free PMC article.
-
A DNA repair pathway can regulate transcriptional noise to promote cell fate transitions.Science. 2021 Aug 20;373(6557):eabc6506. doi: 10.1126/science.abc6506. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Science. 2021. PMID: 34301855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bazar L, Meighen D, Harris V, Duncan R, Levens D, Avigan M (1995) Targeted melting and binding of a DNA regulatory element by a transactivator of c-myc. J Biol Chem 270: 8241–8248 - PubMed
-
- Bentley DL, Groudine M (1986) A block to elongation is largely responsible for decreased transcription of c-myc in differentiated HL60 cells. Nature 321: 702–706 - PubMed
-
- Carey M, Smale ST (2000) Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotes: Concepts, Strategies, and Techniques. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY
-
- Cawley S, Bekiranov S, Ng HH, Kapranov P, Sekinger EA, Kampa D, Piccolboni A, Sementchenko V, Cheng J, Williams AJ, Wheeler R, Wong B, Drenkow J, Yamanaka M, Patel S, Brubaker S, Tammana H, Helt G, Struhl K, Gingeras TR (2004) Unbiased mapping of transcription factor binding sites along human chromosomes 21 and 22 points to widespread regulation of noncoding RNAs. Cell 116: 499–509 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

