SUMO conjugation attenuates the activity of the gypsy chromatin insulator
- PMID: 16628226
- PMCID: PMC1456934
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601068
SUMO conjugation attenuates the activity of the gypsy chromatin insulator
Abstract
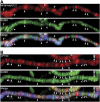
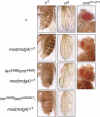
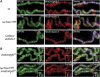
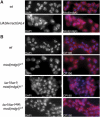
Chromatin insulators have been implicated in the establishment of independent gene expression domains and in the nuclear organization of chromatin. Post-translational modification of proteins by Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier (SUMO) has been reported to regulate their activity and subnuclear localization. We present evidence suggesting that two protein components of the gypsy chromatin insulator of Dorsophila melanogaster, Mod(mdg4)2.2 and CP190, are sumoylated, and that SUMO is associated with a subset of genomic insulator sites. Disruption of the SUMO conjugation pathway improves the enhancer-blocking function of a partially active insulator, indicating that SUMO modification acts to regulate negatively the activity of the gypsy insulator. Sumoylation does not affect the ability of CP190 and Mod(mdg4)2.2 to bind chromatin, but instead appears to regulate the nuclear organization of gypsy insulator complexes. The results suggest that long-range interactions of insulator proteins are inhibited by sumoylation and that the establishment of chromatin domains can be regulated by SUMO conjugation.
Figures



References
-
- Apionishev S, Malhotra D, Raghavachari S, Tanda S, Rasooly RS (2001) The Drosophila UBC9 homologue lesswright mediates the disjunction of homologues in meiosis I. Genes Cells 6: 215–224 - PubMed
-
- Bell AC, Felsenfeld G (2000) Methylation of a CTCF-dependent boundary controls imprinted expression of the Igf2 gene. Nature 405: 482–485 - PubMed
-
- Capelson M, Corces VG (2005) The ubiquitin ligase dTopors directs the nuclear organization of a chromatin insulator. Mol Cell 20: 105–116 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

