Fragmented left sided QRS in absence of bundle branch block: sign of left ventricular aneurysm
- PMID: 16630087
- PMCID: PMC7313312
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1542-474X.2006.00094.x
Fragmented left sided QRS in absence of bundle branch block: sign of left ventricular aneurysm
Abstract
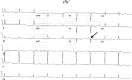
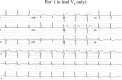
Background: A left ventricular aneurysm (LVA) occurs between 3.5% and 9.4% of all cases of acute myocardial infarction. A fragmented left sided QRS (RSR; pattern or its variant RSr;, rSR;, or rSr;) without evidence of bundle branch block (QRS duration <or=120 ms) on the ECG may be associated with a significant myocardial scar, which is the characteristic of a LVA. We, therefore, postulate that fragmented QRS (RSR; pattern or its variant) in the left sided leads (I, aVL, V(3) to V(6)) may be a useful sign of LVA.
Methods: ECGs of 110 consecutive patients with LVA documented by left ventricular angiography (30 degrees right anterior oblique view) was compared with 220 patients without LVA (110 patients with and 110 patients without coronary artery disease (CAD)), who were evaluated for CAD by symptoms and signs.
Results: The sensitivity of the fragmented QRS for identification of LVA was 50% (55 of 110 patients) and specificity was 94.6% (209 of 220). Within the study population, the positive predictive value of the fragmented QRS for LVA was 83.3% (55 of 66) and the negative predictive value was 79.2% (209 of 264). Based on the range of prevalence of LVA in postmyocardial infarction population (3.5-9.4%) and on observed sensitivity and specificity, the positive predictive value of fragmented QRS for LVA after infarction can be estimated at 29-53% and the negative predictive value can be estimated at 95-98%.
Conclusion: The sensitivity of fragmented QRS in left precordial leads for LVA was only 50%, whereas the specificity was 94.5%. It has a relatively low to moderate positive predictive value and high negative predictive value.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Non-Q-wave-electrocardiograms. Signs of earlier myocardial infarction].Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2012 Nov;107(8):634-40. doi: 10.1007/s00063-012-0127-9. Epub 2012 Aug 1. Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2012. PMID: 22847458 Review. German.
-
Diagnosis of ventricular aneurysm and other severe segmental left ventricular dysfunction consequent to a myocardial infarction in the presence of right bundle branch block: ECG correlates of a positive diagnosis made via echocardiography and/or contrast ventriculography.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2005 Jan;10(1):53-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1542-474X.2005.00590.x. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2005. PMID: 15649238 Free PMC article.
-
T/QRS ratio best distinguishes ventricular aneurysm from anterior myocardial infarction.Am J Emerg Med. 2005 May;23(3):279-87. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2005.01.003. Am J Emerg Med. 2005. PMID: 15915398
-
Fragmented wide QRS on a 12-lead ECG: a sign of myocardial scar and poor prognosis.Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2008 Oct;1(4):258-68. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.107.763284. Epub 2008 Jul 14. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2008. PMID: 19808417
-
[Wide QRS complex tachycardia: an old and new problem].G Ital Cardiol (Rome). 2009 Sep;10(9):580-95. G Ital Cardiol (Rome). 2009. PMID: 19891250 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
[Non-Q-wave-electrocardiograms. Signs of earlier myocardial infarction].Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2012 Nov;107(8):634-40. doi: 10.1007/s00063-012-0127-9. Epub 2012 Aug 1. Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2012. PMID: 22847458 Review. German.
-
Relationship between fragmented QRS complexes and left ventricular systolic and diastolic functions.Herz. 2013 Sep;38(6):665-70. doi: 10.1007/s00059-012-3739-1. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Herz. 2013. PMID: 23588600
-
Role of QRS Fragmentation for Risk Stratification in Adults With Tetralogy of Fallot.J Am Heart Assoc. 2018 Dec 18;7(24):e010274. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.010274. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018. PMID: 30561260 Free PMC article.
-
[Fragmented QRS. Relevance in clinical practice].Herzschrittmacherther Elektrophysiol. 2015 Sep;26(3):235-41. doi: 10.1007/s00399-015-0390-6. Herzschrittmacherther Elektrophysiol. 2015. PMID: 26249048 German.
-
Absence and Resolution of Fragmented QRS Predict Reversible Myocardial Ischemia With Higher Probability of ST Segment Resolution in Patients With ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction.Korean Circ J. 2012 Oct;42(10):674-83. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2012.42.10.674. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Korean Circ J. 2012. PMID: 23170095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mariotti R, Petronio AS, Robiglio L, et al Left ventricular aneurysm: Clinical and hemodynamic data. Clin Cardiol 1990;13(12):845 – 850. - PubMed
-
- Castany R, Cerene A, Puel P. Left ventricular aneurysm resulting from myocardial infarction. J Cardiovas Surg 1974;18: 74 – 81. - PubMed
-
- Su X, Sekiguchi M, Endo M. An ultrastructural study of cardiac myocytes in postmyocardial infarction ventricular aneurysm representative of chronic ischemic myocardium using semiquantitative and quantitative assessment. Cardiovasc Pathol 2000;9(1):1 – 8. - PubMed
-
- Friedman BM, Dunn MI. Postinfarction ventricular aneurysms. Clin Cardiol 1995;18(9):505 – 511. - PubMed
-
- Grossi EA, Chinitz LA, Galloway AC, et al Endoventricular remodeling of left ventricular aneurysm. Functional, clinical, and electrophysiological result. Circulation 1995;92: 98 – 100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

