Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor as a novel targeting molecule for cancer therapy
- PMID: 16630129
- PMCID: PMC11159358
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00188.x
Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor as a novel targeting molecule for cancer therapy
Abstract
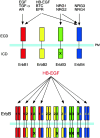
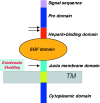
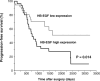
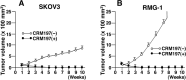
HB-EGF, a member of the EGF family of growth factors, exerts its biological activity through activation of the EGFR and other ErbB receptors. HB-EGF participates in diverse biological processes, including heart development and maintenance, skin wound healing, eyelid formation, blastocyst implantation, progression of atherosclerosis and tumor formation, through the activation of signaling molecules downstream of ErbB receptors and interactions with molecules associated with HB-EGF. Recent studies have indicated that HB-EGF gene expression is significantly elevated in many human cancers and its expression level in a number of cancer-derived cell lines is much higher than those of other EGFR ligands. Several lines of evidence have indicated that HB-EGF plays a key role in the acquisition of malignant phenotypes, such as tumorigenicity, invasion, metastasis and resistance to chemotherapy. Studies in vitro and in vivo have indicated that HB-EGF expression is essential for tumor formation of cancer-derived cell lines. CRM197, a specific inhibitor of HB-EGF, and an antibody against HB-EGF are both able to inhibit tumor growth in nude mice. These results indicate that HB-EGF is a promising target for cancer therapy, and that the development of targeting tools against HB-EGF could represent a novel type of therapeutic strategy, as an alternative to targeting ErbB receptors.
Figures
References
-
- Riese DJ 2nd, Stern DF. Specificity within the EGF family/ErbB receptor family signaling network. Bioessays 1998; 20: 41–8. - PubMed
-
- Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001; 2: 127–37. - PubMed
-
- Schlessinger J. Common and distinct elements in cellular signaling via EGF and FGF receptors. Science 2004; 306: 1506–7. - PubMed
-
- Hynes NE, Lane HA. ERBB receptors and cancer: the complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer 2005; 5: 341–54. - PubMed
-
- Mosesson Y, Yarden Y. Oncogenic growth factor receptors: implications for signal transduction therapy. Semin Cancer Biol 2004; 14: 262–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

