Detection of germline deletions using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction in Japanese patients with von Hippel-Lindau disease
- PMID: 16630138
- PMCID: PMC11159241
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00193.x
Detection of germline deletions using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction in Japanese patients with von Hippel-Lindau disease
Abstract
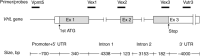
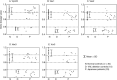
Germline mutations of the VHL gene are responsible for VHL. Approximately 70% of VHL families display small intragenic mutations detectable by sequencing, whereas partial- or whole-gene deletions have been described in the majority of the remaining families. For such large deletions, complex genetic techniques other than sequencing might have to be used. In this study, we describe an RQ-PCR assay with TaqMan fluorescent probes to detect germline VHL deletions. The RQ-PCR primer/probe sets were designed for the three VHL coding exons as well as for the 5' promoter and 3' untranslated regions. The RQ-PCR assay for 30 normal and 10 known VHL deletion control samples demonstrated high sensitivity and specificity. We then screened 29 individuals from 19 classical VHL families (16 type 1, 2 type 2A, and one type 2B) and one PHEO family, as well as four solitary suspected cases, none displaying any sequence changes, for VHL deletions by the RQ-PCR assay. We detected germline deletions in 17 (89%) classical families including 15 type 1, one type 2A, and one type 2B. We also identified two mutation carriers and two non-carriers in our family cohort. The one PHEO family and four solitary cases did not display any deletion patterns. These findings indicated that the TaqMan-based RQ-PCR assay is a simple and potent technique for the rapid, sensitive, and specific investigation of VHL genetic diagnoses that could be used profitably before more complex large-deletion detection techniques.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Germline mutations in the von Hippel-Lindau disease (VHL) gene in mainland Chinese families.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2008 Nov;134(11):1211-8. doi: 10.1007/s00432-008-0399-x. Epub 2008 Apr 30. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18446368 Free PMC article.
-
Family history of von Hippel-Lindau disease was uncommon in Chinese patients: suggesting the higher frequency of de novo mutations in VHL gene in these patients.J Hum Genet. 2012 Apr;57(4):238-43. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2012.10. Epub 2012 Feb 23. J Hum Genet. 2012. PMID: 22357542
-
[Large germline deletion of the VHL gene in Chinese families with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome].Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2009 Oct;26(5):539-41. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1003-9406.2009.05.014. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 19806577 Chinese.
-
Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. A pleomorphic condition.Cancer. 1999 Dec 1;86(11 Suppl):2478-82. Cancer. 1999. PMID: 10630173 Review.
-
Genotype-phenotype correlation in von Hippel-Lindau syndrome.Hum Mol Genet. 2001 Apr;10(7):763-7. doi: 10.1093/hmg/10.7.763. Hum Mol Genet. 2001. PMID: 11257110 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic screening for von Hippel-Lindau gene mutations in non-syndromic pheochromocytoma: low prevalence and false-positives or misdiagnosis indicate a need for caution.Horm Metab Res. 2012 May;44(5):343-8. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1304662. Epub 2012 Mar 21. Horm Metab Res. 2012. PMID: 22438210 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and molecular characterization of Brazilian families with von Hippel-Lindau disease: a need for delineating genotype-phenotype correlation.Fam Cancer. 2010 Dec;9(4):635-42. doi: 10.1007/s10689-010-9357-2. Fam Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20567917
-
Surgical resection of double advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors with multiple renal cell carcinoma associated with von Hippel-Lindau disease.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2024 Aug;17(4):697-704. doi: 10.1007/s12328-024-01967-2. Epub 2024 May 2. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38693425
-
Familial neuroendocrine tumor syndromes: from genetics to clinical practice.Pituitary. 2006;9(3):231-6. doi: 10.1007/s11102-006-0268-z. Pituitary. 2006. PMID: 17001463 Review.
-
Relationship between ZHX2 Expression and VHL Gene Alteration in VHL-associated and Sporadic Hemangioblastomas of the Central Nervous System.J Kidney Cancer VHL. 2024 Dec 31;11(4):39-47. doi: 10.15586/jkcvhl.v11i4.355. eCollection 2024. J Kidney Cancer VHL. 2024. PMID: 39850947 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lonser RR, Glenn GM, Walther M et al. Von Hippel–Lindau disease. Lancet 2003; 361: 2059–67. - PubMed
-
- Maher ER. Von Hippel–Lindau disease. Curr Mol Med 2004; 4: 833–42. - PubMed
-
- Latif F, Tory K, Gnarra J et al. Identification of the von Hippel‐Lindau disease tumor suppressor gene. Science 1993; 260: 1317–20. - PubMed
-
- Zbar B, Kishida T, Chen F et al. Germline mutations in the Von Hippel–Lindau disease (VHL) gene in families from North America, Europe, and Japan. Hum Mutat 1996; 8: 348–57. - PubMed
-
- Zbar B, Kaelin W, Maher E, Richard S. Third International Meeting on von Hippel–Lindau disease. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 2251–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

