Rosuvastatin treatment protects against nitrate-induced oxidative stress in eNOS knockout mice: implication of the NAD(P)H oxidase pathway
- PMID: 16633368
- PMCID: PMC1751785
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706738
Rosuvastatin treatment protects against nitrate-induced oxidative stress in eNOS knockout mice: implication of the NAD(P)H oxidase pathway
Abstract
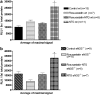
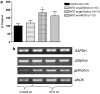
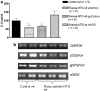
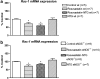
Nitrate tolerance is associated with an enhanced superoxide anion (O(2)(-)) production and may be attenuated by statins as they interact with the two main endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) and NAD(P)H oxidase pathways involved in this oxidative stress. Groups of wild-type (wt, C57Bl/6J) and eNOS knock-out mice (eNOS(-/-)) received rosuvastatin (20 mg kg(-1) day(-1) p.o.) for 5 weeks and a cotreatment with the statin plus nitroglycerin (NTG; 30 mg kg(-1) day(-1), subcutaneous injections b.i.d.) for the last 4 days. Another group received only NTG (30 mg kg(-1) d(-1), b.i.d. for 4 days) and finally control mice from both strains received no treatment. Rings of thoracic aortas from these groups were studied in organ baths. Relaxations to NTG (0.1 nM-0.1 mM) were determined on thromboxane analogue (U44619)-precontracted rings and O(2)(-) production (RLU 5 s(-1) mg(-1) of total protein content) was assessed in aorta homogenates with the lucigenin-enhanced chemiluminescence technique. Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction analysis was performed on aortas from both mice strains. In vivo NTG treatment induced a significant rightward shift of the concentration-effect curve to NTG compared to control group. There was, however, no cross-tolerance with non-nitrate sources of NO (unaltered response to acetylcholine in wt group). The rosuvastatin + NTG cotreatment was able to protect against the development of nitrate tolerance in both mice strains and L-mevalonate abolished this protective effect of rosuvastatin. In vivo treatment with apocynin, a purported NAD(P)H oxidase inhibitor, also produced a similar protection to that observed with rosuvastatin in both strains. Superoxide anion formation was increased after NTG treatment in both mice strains and the rosuvastatin + NTG cotreatment was able to reduce that production. Moreover, rosuvastatin treatment abolished the increase in gp91phox mRNA (an endothelial membrane NAD(P)H oxidase subunit) expression induced by in vivo exposure to NTG. These findings suggest that long-term rosuvastatin treatment protects against nitrate tolerance by counteracting NTG-induced increase in O(2)(-) production, probably via a direct interaction with the NAD(P)H oxidase pathway.
Figures
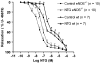


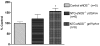
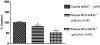
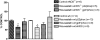
References
-
- ANNING P.B., COLES B., BERMUDEZ-FAJARDO A., MARTIN P.E., LEVISON B.S., HAZEN S.L., FUNK C.D., KUHN H., O'DONNELL V.B. Elevated endothelial nitric oxide bioactivity and resistance to angiotensin-dependent hypertension in 12/15-lipoxygenase knockout mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2005;166:653–662. - PMC - PubMed
-
- ARRUDA R.M., PEOTTA V.A., MEYRELLES S.S., VASQUEZ E.C. Evaluation of vascular function in apolipoprotein E knockout mice with angiotensin-dependent renovascular hypertension. Hypertension. 2005;46:932–936. - PubMed
-
- BAYRAKTUTAN U., BLAYNEY L., SHAH A.M. Molecular characterization and localization of the NAD(P)H oxidase components gp91-phox and p22-phox in endothelial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000;20:1903–1911. - PubMed
-
- BAYRAKTUTAN U., DRAPER N., LANG D., SHAH A.M. Expression of functional neutrophil-type NADPH oxidase in cultured rat coronary microvascular endothelial cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 1998;38:256–262. - PubMed
-
- BEN-SHAUL V., LOMNITSKI L., NYSKA A., ZUROVSKY Y., BERGMAN M., GROSSMAN S. The effect of natural antioxidants, NAO and apocynin, on oxidative stress in the rat heart following LPS challenge. Toxicol. Lett. 2001;123:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

