Nitric oxide-GAPDH-Siah: a novel cell death cascade
- PMID: 16633896
- PMCID: PMC11520605
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-006-9011-6
Nitric oxide-GAPDH-Siah: a novel cell death cascade
Abstract
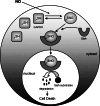
1. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) is an extremely abundant glycolytic enzyme, and exemplifies the class of proteins with multiple, seemingly unrelated functions. Recent studies indicate that it is a major intracellular messenger mediating apoptotic cell death. This paper reviews the GAPDH cell death cascade and discusses its clinical relevance. 2. A wide range of apoptotic stimuli activate NO formation, which S-nitrosylates GAPDH. The S-nitrosylation abolishes catalytic activity and confers upon GAPDH the ability to bind to Siah, an E3-ubiquitin-ligase, which translocates GAPDH to the nucleus. In the nucleus, GAPDH stabilizes the rapidly turning over Siah, enabling it to degrade selected target proteins and affect apoptosis. 3. The cytotoxicity of mutant Huntingtin (mHtt) requires nuclear translocation which appears to be mediated via a ternary complex of GAPDH-Siah-mHtt. The neuroprotective actions of the monoamine oxidase inhibitor R-(-)-deprenyl (deprenyl) reflect blockade of GAPDH-Siah binding. Thus, novel cytoprotective therapies may emerge from agents that prevent GAPDH-Siah binding.
Figures
References
-
- Brown, V. M., Krynetski, E. Y., Krynetskaia, N. F., Grieger, D., Mukatira, S. T., Murti, K. G., Slaughter, C. A., Park, H. W., and Evans, W. E. (2004). A novel CRM1-mediated nuclear export signal governs nuclear accumulation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase following genotoxic stress. J. Biol. Chem.279:5984–5992. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

